1.结论
照惯例,先上结论,再说过程,不想看过程的可直接略过。
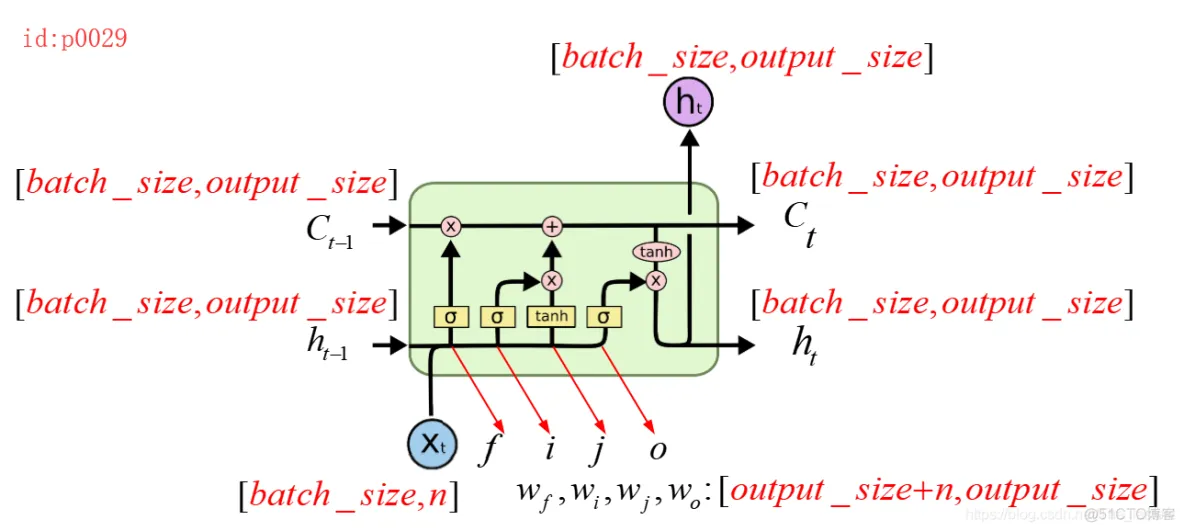
从这个图我们可以知道,一个LSTM cell中有4个参数,并且形状都是一样的shape=[output_size+n,output_size],其中n表示输入张量的维度,output_size通过函数BasicLSTMCell(num_units=output_size)获得。
2.怎么来的?
让我们一步一步从Tensorflow的源码中来获得这些信息!
2.1 cell.state_size
首先,需要明白Tensorflow中,state表示的是cell中有几个状态。例如在BasicRNNCell中,state就只有h这一个状态;而在BasicLSTMCell中,state就有h和c这两个状态。其次,state_size表示的是每个状态的第二维度,也就是output_size。
举例:
import tensorflow as tfoutput_size = 10batch_size = 32dim = 50cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=output_size)print(cell.state_size)>>LSTMStateTuple(c=10, h=10)1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.LSTMStateTuple(c=10, h=10)就表示,c和h的output_size都为10,即[batch_size,10]。另外Tensorflow在实现的时候,都将c,h困在一起了,即以Tuple的方式,这也是Tensorflow所推荐的。
2.2 cell.zero_state
在LSTM中,zero_state就自然对应两个部分了, h 0 , c 0 h_0,c_0 h0,c0。
import tensorflow as tfoutput_size = 10batch_size = 32dim = 50cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=output_size)input = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[batch_size, 50])h0 = cell.zero_state(batch_size=batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)print(h0)>>LSTMStateTuple(c=<tf.Tensor 'BasicLSTMCellZeroState/zeros:0' shape=(32, 10) dtype=float32>,h=<tf.Tensor 'BasicLSTMCellZeroState/zeros_1:0' shape=(32, 10) dtype=float32>)1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.可以看到,返回了c,h两个零状态!
2.3 关键性的一步cell.call
先说明一点,由于源码很多,所有在下面的讲解中只会列出函数名和对应核心的代码,具体可以跳转至call的实现部分。
import tensorflow as tfoutput_size = 10batch_size = 32dim = 50cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=output_size)input = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[batch_size, 50])h0 = cell.zero_state(batch_size=batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)new_h, new_state = cell.call(input, h0)------------------------------------------------------------------def call(self, inputs, state): if self._state_is_tuple: c, h = state concat = _linear([inputs, h], 4 * self._num_units, True) # i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(value=concat, num_or_size_splits=4, axis=1) new_c = ( c * sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) + sigmoid(i) * self._activation(j)) new_h = self._activation(new_c) * sigmoid(o) if self._state_is_tuple: new_state = LSTMStateTuple(new_c, new_h) else: new_state = array_ops.concat([new_c, new_h], 1) return new_h, new_state1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.首先,从call()中的第17行代码可知,首先从state中得到传进来的c,h,然后就开始进行第18行的操作了,为了弄清楚里面到底干了啥,于是我们再次进入_linear()这个函数。
总的来说,_linear()这个函数实现了:先将 h , x h,x h,x进行concat,然后进行线性变换;如下图所示:
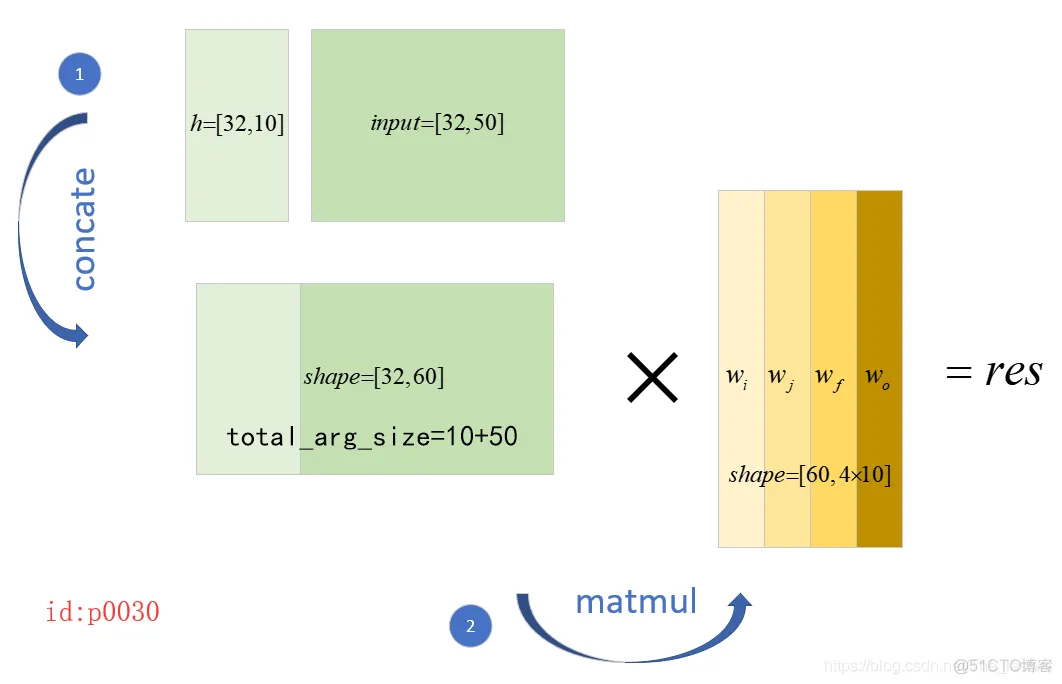
而与上面两个步骤对应代码就是下面的
concat = _linear([inputs, h], 4 * self._num_units, True)def _linear(args, output_size, bias, # 是否要添加偏置 bias_initializer=None, kernel_initializer=None): shapes = [a.get_shape() for a in args]# 得到传进来的inputs,h的shape total_arg_size += shape[1].value # 得到inputs和h一共有多少列 res = math_ops.matmul(array_ops.concat(args, 1), weights)# 同时计算得到4个部分的线性映射1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.其中, w i , w j , w f , w o w_i,w_j,w_f,w_o wi,wj,wf,wo就是LSTM cell中的4个权重参数。
现在我们已经清楚了_linear()的作用,接下来我们就再次回到 c a l l ( ) call() call()这个函数中:
def call(self, inputs, state): if self._state_is_tuple: c, h = state concat = _linear([inputs, h], 4 * self._num_units, True) # i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(value=concat, num_or_size_splits=4, axis=1) new_c = ( c * sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) + sigmoid(i) * self._activation(j)) new_h = self._activation(new_c) * sigmoid(o) if self._state_is_tuple: new_state = LSTMStateTuple(new_c, new_h) else: new_state = array_ops.concat([new_c, new_h], 1) return new_h, new_state1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.经过上面第4行代码,我们得到了4个部分线性变换后的结果;然后根据第6行代码可以看出,将concat又分割成了四个部分,而这四个部分对应关系如下图所示:
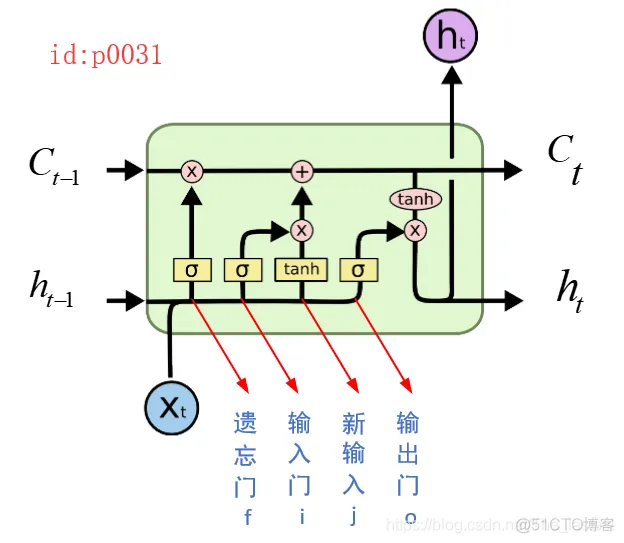
接着第7,9行代码就分别计算出了new_c,new_h
3. 总结
import tensorflow as tfoutput_size = 10batch_size = 32dim = 50cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=output_size)input = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[batch_size, 50])h0 = cell.zero_state(batch_size=batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)new_h, new_state = cell.call(input, h0)1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.对于一个基本的LSTM cell,在定义的时候,通过上面第6行代码的num_units,第8行的batch_size和第7行的input我们就得到了cell中所有参数的shape。
对于LSTM按时间维度展开的方法和多层堆叠同BasicRNNCell一致
免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删