我整理的一些关于【深度学习,机器学习,Python,TensorFlow】的项目学习资料(附讲解~~)和大家一起分享、学习一下:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
(train_image, train_lable),(test_image, test_label) = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data() # 加载fashion_mnist数据
# 显示部分数据集
def show_imgs(n_rows, n_cols, x_data, y_data, class_names):
assert len(x_data) == len(y_data)
assert n_rows * n_cols < len(y_data)
plt.figure(figsize = (n_cols * 1.4, n_cols * 1.6))
for row in range(n_rows):
for col in range(n_cols):
index = n_cols * row + col
plt.subplot(n_rows, n_cols, index+1)
plt.imshow(x_data[index], cmap='binary', interpolation = 'nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title(class_names[y_data[index]])
plt.show()
class_names = ['T-shirt', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
show_imgs(3, 9, train_image, train_lable, class_names)
运行的结果如下图所示:可以发现他们有10种不同的类别。

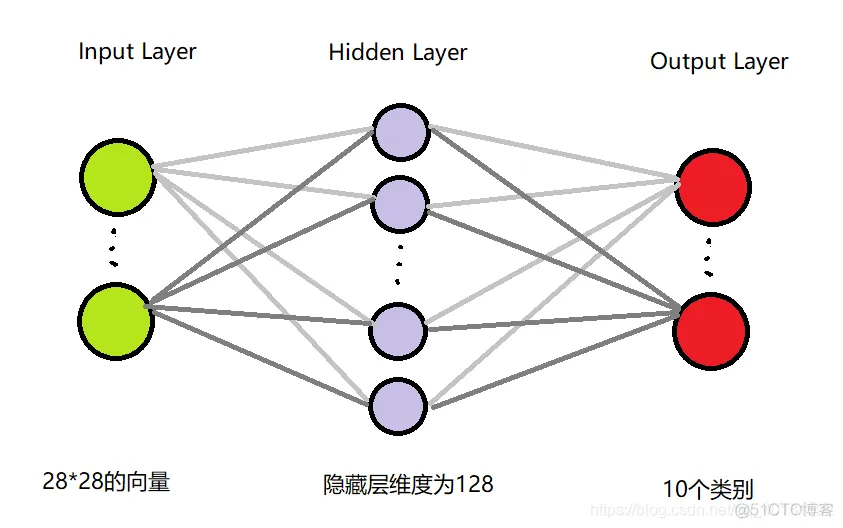
由于每一张图片维度都是28*28,所以输入层的单元数为28*28;因为是一张图片图像,像素比较多,故需要隐藏层维度大一点在此先设置为128,后面会说明隐藏层的大小对其结果的影响;输出层维度为10,因为有十个类别,最后可以通过softmax将其转化为10个概率,概率最大的那一个就是最佳的类别。
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28,28)))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'))
常用的激活函数有:‘relu’、‘sigmoid’、‘tanh’、‘Leak relu’
sigmoid函数
Sigmoid函数是一个在生物学中常见的S型函数,也称为S型生长曲线。在信息科学中,由于其单增以及反函数单增等性质,Sigmoid函数常被用作神经网络的阈值函数,将变量映射到0,1之间。公式如下
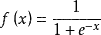
函数图像如下

tanh函数
Tanh是双曲函数中的一个,Tanh()为双曲正切。在数学中,双曲正切“Tanh”是由基本双曲函数双曲正弦和双曲余弦推导而来。公式如下
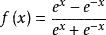
函数图像如下
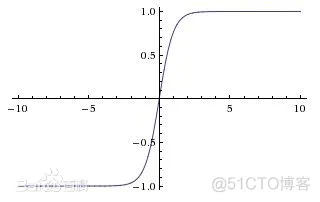
relu函数
Relu激活函数(The Rectified Linear Unit),用于隐层神经元输出。公式如下
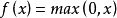
函数图像如下
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
model.summary()来查看建立的模型的结构:Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
flatten (Flatten) (None, 784) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 128) 100480
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290
=================================================================
Total params: 101,770
Trainable params: 101,770
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
None
可以发现每一层的维度大小都有给出,包括每一层的参数个数paramters,这里隐藏层的参数为100480 = (784 + 1)* 128,原因是前面的神经网络的介绍中已经说明,需要多加一个偏置单元,同理后面的1290 = (128 + 1)* 10,也默认添加了一个偏置单元。
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['acc'])
optimizer:是优化方法,常用的优化方法有adam、SGD(随机梯度下降优化器)、RMSprop等;
loss:是损失函数,常用的有’mes’(均方差),这里由于是分类问题,使用的是前面所讨论的交叉熵损失函数,有两种’sparse_categorical_crossentropy’(适用于最后分类的顺序编码)、‘categorical_crossentropy’(适用于最后分类是独热编码);
metrics=[‘acc’]可查看每一次的准确率;
history = model.fit(train_image, train_lable, epochs=5,validation_data=(test_image,test_label))
epochs为训练代数,前面是训练集,后面是验证集。每次训练的结果都存在history里面,后面可以根据history将学习曲线以及准确率曲线画出来。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
(train_image, train_lable),(test_image, test_label) = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data() # 加载fashion_mnist数据
def show_imgs(n_rows, n_cols, x_data, y_data, class_names):
assert len(x_data) == len(y_data)
assert n_rows * n_cols < len(y_data)
plt.figure(figsize = (n_cols * 1.4, n_cols * 1.6))
for row in range(n_rows):
for col in range(n_cols):
index = n_cols * row + col
plt.subplot(n_rows, n_cols, index+1)
plt.imshow(x_data[index], cmap='binary', interpolation = 'nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title(class_names[y_data[index]])
plt.show()
def plot_learning_curves(history):
pd.DataFrame(history.history).plot(figsize=(8,5))
plt.grid(True)
plt.gca().set_ylim(0, 1)
plt.show()
class_names = ['T-shirt', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
show_imgs(3, 9, train_image, train_lable, class_names)
# 归一化
train_image = train_image/255
test_image = test_image/255
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28,28))) # 28*28向量 将矩阵转化为向量
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['acc'])
history = model.fit(train_image, train_lable, epochs=5,validation_data=(test_image,test_label))
plot_learning_curves(history)
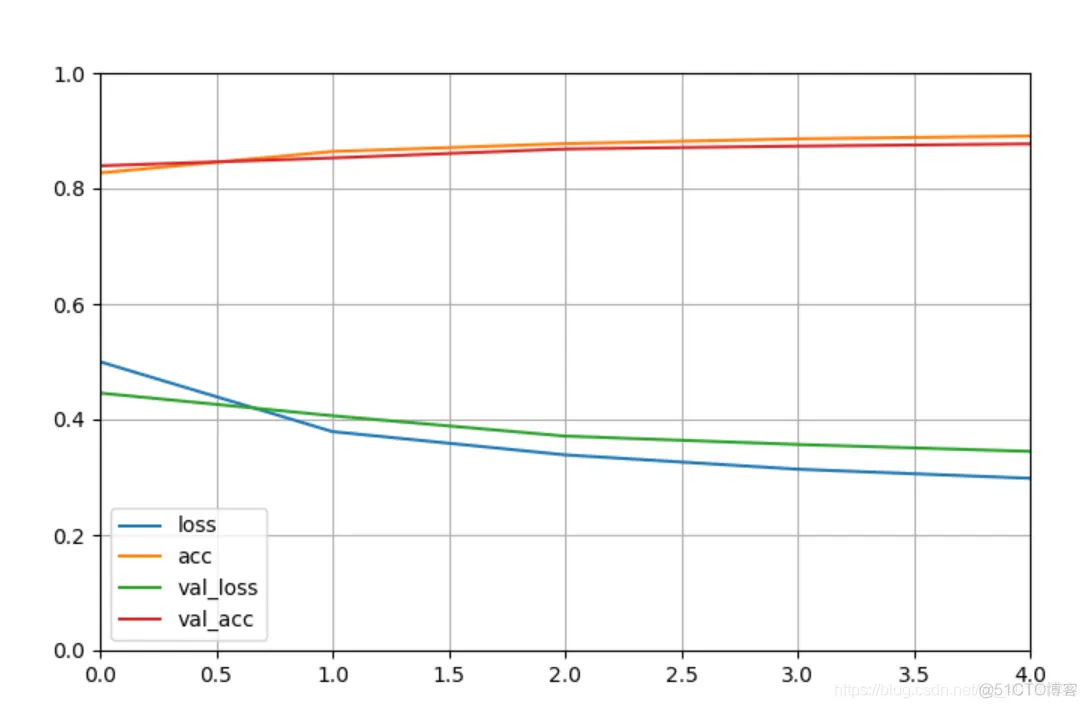
通过输出的结果可以发现loss: 0.2982 - acc: 0.8909 - val_loss: 0.3448 - val_acc: 0.8773,准确度为0.89,测试集的准确度为0.87。
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28,28))) # 28*28向量 将矩阵转化为向量
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)) # 添加Dropout层抑制过拟合
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
就是在之前搭建的神经网络模型的基础上添加一层,参数为0.5代表抑制程度,Dropout的基本原理就是按照一定方法去掉一些神经元,使网络变简单,从而可以抑制过拟合。
logdir = './callbacks' # 如果报错改为绝对路径
if not os.path.exists(logdir):
os.mkdir(logdir)
output_model_file = os.path.join(logdir,'fashion_mnist_model.h5')
其他的callbacks请参考 https://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/other/callbacks/官方中文文档
tensorboard --logdir=/full_path_to_your_logsfilepathfilepath可以是格式化的字符串,里面的占位符将会被epoch值和传入on_epoch_end的logs关键字所填入logdir = './callbacks'
if not os.path.exists(logdir):
os.mkdir(logdir)
output_model_file = os.path.join(logdir,'fashion_mnist_model.h5')
callbacks = [ tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(logdir),
tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(output_model_file,save_best_only=True),]
history = model.fit(train_image, train_lable, epochs=5,validation_data=(test_image,test_label),callbacks = callbacks)
tensorboard --logdir=callbacks生成的本地网页数据:http://localhost:6006/(通过端口6006在网页中打开)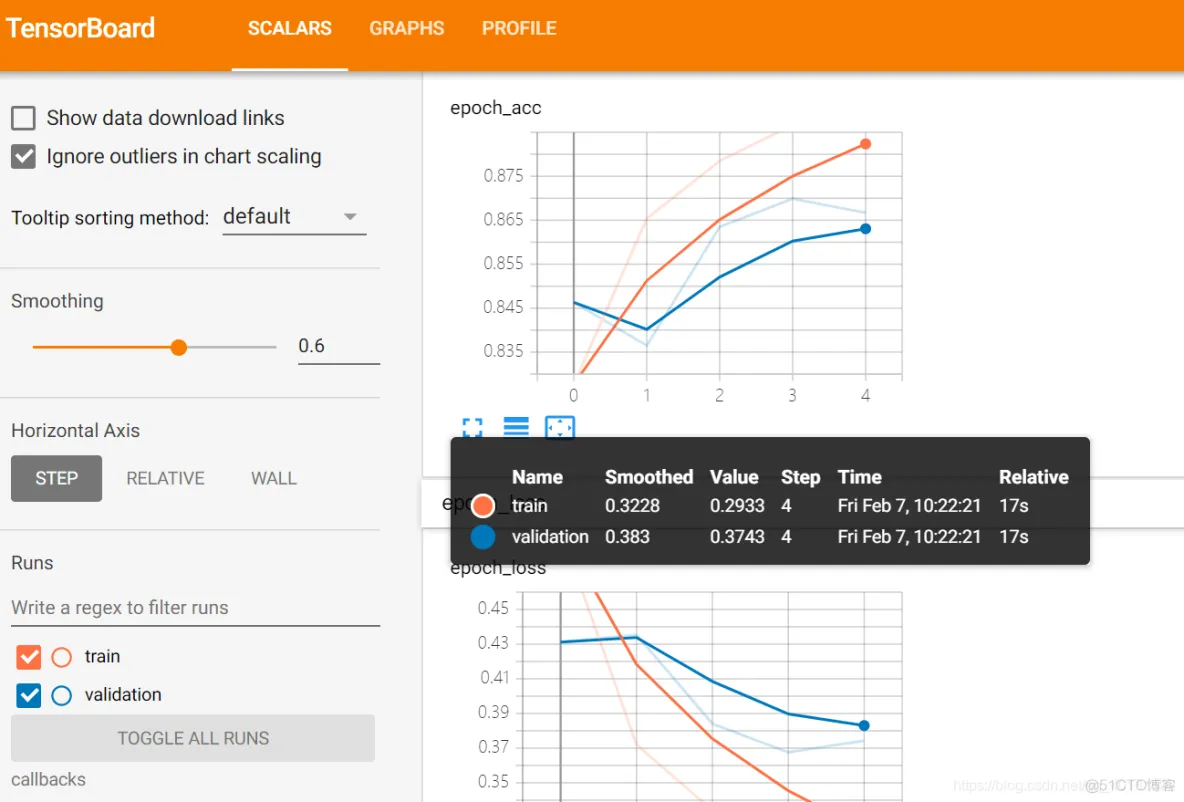
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
def generate_data(): # 产生数据集
np.random.seed(0)
X, y = datasets.make_moons(200, noise=0.20) # 产生月牙形状的数据集
return X, y
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y): # 画决策边界线
# 设置图像边界最大值与最小值
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
h = 0.01 #采样间隔
# 生成网格矩阵
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
#sample = next(iter(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]))
pred = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
pred = tf.argmax(pred, axis=1)
pred_numpy = pred.numpy()
# 对整个网格矩阵进行预测
Z = pred_numpy.reshape(xx.shape) # 使预测结果重新变成网格数组大小
# 画出决策边界
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
# 画出数据点
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s = 20,c=y, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
def main():
X, y = generate_data()
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(2, )))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation='tanh'))
# model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)) # 添加Dropout层抑制过拟合
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(2, activation='softmax'))
print(model.summary())
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['acc'])
history = model.fit(X, y, epochs=2000)
model.evaluate(X,y)
plt.plot(history.epoch,history.history.get('loss'))
plt.figure(2)
plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
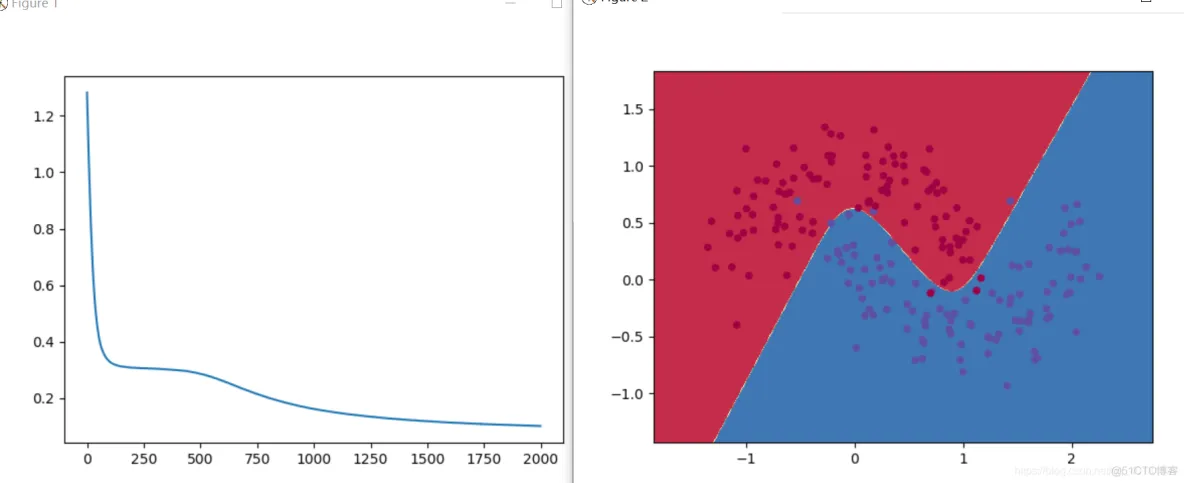
可以发现代码量大大减少,并且得到了和之前相同的效果,并且在这里可以很方便的修改参数(隐藏层维度,隐藏层数量,激活函数等等)
免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删