产品
这里将加载iris数据集,创建一个山鸢尾花(I.setosa)的分类器。
# Nonlinear SVM Example#----------------------------------## This function wll illustrate how to
# implement the gaussian kernel on# the iris dataset.#
# Gaussian Kernel:# K(x1, x2) = exp(-gamma * abs(x1 - x2)^2)import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as
npimport tensorflow as tffrom sklearn import datasetsfrom tensorflow.python
.framework import opsops.reset_default_graph()# Create graphsess = tf.Session()
# Load the data# iris.data = [(Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width)]
# 加载iris数据集,抽取花萼长度和花瓣宽度,分割每类的x_vals值和y_vals值iris = datasets.load_iris()x_vals = np
.array([[x[0], x[3]] for x in iris.data])y_vals = np.array([1 if y==0 else -1 for y in iris
.target])class1_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]class1_y = [x[1] for i,x in
enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]class2_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals)
if y_vals[i]==-1]class2_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==-1]
# Declare batch size# 声明批量大小(偏向于更大批量大小)batch_size = 150
# Initialize placeholdersx_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf
.float32)y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf
.float32)prediction_grid = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32)
# Create variables for svmb = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,batch_size]))
# Gaussian (RBF) kernel# 声明批量大小(偏向于更大批量大小)gamma = tf.constant(-25.0)sq_dists = tf
.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(x_data)))my_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(sq_dists)))
# Compute SVM Modelfirst_term = tf.reduce_sum(b)b_vec_cross = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(b), b)
y_target_cross = tf.matmul(y_target, tf.transpose(y_target))second_term = tf
.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(my_kernel, tf.multiply(b_vec_cross, y_target_cross)))loss = tf.negative(tf
.subtract(first_term, second_term))# Gaussian (RBF) prediction kernel# 创建一个预测核函数rA = tf
.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1),[-1,1])rB = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(prediction_grid),
1),[-1,1])pred_sq_dist = tf.add(tf.subtract(rA, tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf
.transpose(prediction_grid)))), tf.transpose(rB))pred_kernel = tf
.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(pred_sq_dist)))
# 声明一个准确度函数,其为正确分类的数据点的百分比prediction_output = tf.matmul(tf
.multiply(tf.transpose(y_target),b), pred_kernel)prediction = tf.sign(prediction_output-tf
.reduce_mean(prediction_output))accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.squeeze(prediction), tf
.squeeze(y_target)), tf.float32))# Declare optimizermy_opt = tf.train.
GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)# Initialize variablesinit = tf
.global_variables_initializer()sess.run(init)
# Training looploss_vec = []batch_accuracy = []for i in range(300): rand_index = np
.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size) rand_x = x_vals[rand_index] rand_y = np
.transpose([y_vals[rand_index]]) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) loss_vec.append(temp_loss)
acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x,
y_target: rand_y, prediction_grid:rand_x})
batch_accuracy.append(acc_temp) if (i+1)%75==0: print('Step #' + str(i+1))
print('Loss = ' + str(temp_loss))# Create a mesh to plot points in# 为了绘制决策边界(Decision Boundary),
我们创建一个数据点(x,y)的网格,评估预测函数x_min, x_max = x_vals[:, 0].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 0].max() + 1y_min
, y_max = x_vals[:, 1].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 1].max() + 1xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))grid_points = np
.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()][grid_predictions] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x,
y_target: rand_y,
prediction_grid: grid_points})grid_predictions = grid_predictions.reshape(xx.shape)
# Plot points and gridplt.contourf(xx, yy, grid_predictions,
cmap=plt.cm.Paired, alpha=0.8)plt.plot(class1_x, class1_y, 'ro', label='I. setosa')plt.plot(class2_x,
class2_y, 'kx', label='Non setosa')plt.title('Gaussian SVM Results on Iris Data')plt
.xlabel('Pedal Length')plt.ylabel('Sepal Width')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.ylim([-0.5, 3.0])plt
.xlim([3.5, 8.5])plt.show()# Plot batch accuracyplt.plot(batch_accuracy, 'k-', label='Accuracy')plt
.title('Batch Accuracy')plt.xlabel('Generation')plt.ylabel('Accuracy')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt
.show()# Plot loss over timeplt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-')plt.title('Loss per Generation')plt
.xlabel('Generation')plt.ylabel('Loss')plt.show()1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.
23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.
58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.
93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.114.115.116.117.118.119.120.
121.122.123.124.125.126.127.128.129.130.131.132.133.134.135.输出:
Step #75Loss = -110.332Step #150Loss = -222.832Step #225Loss = -335.332Step #300Loss = -447.8321.2.3.4.5.
6.7.8.四种不同的gamma值(1,10,25,100):
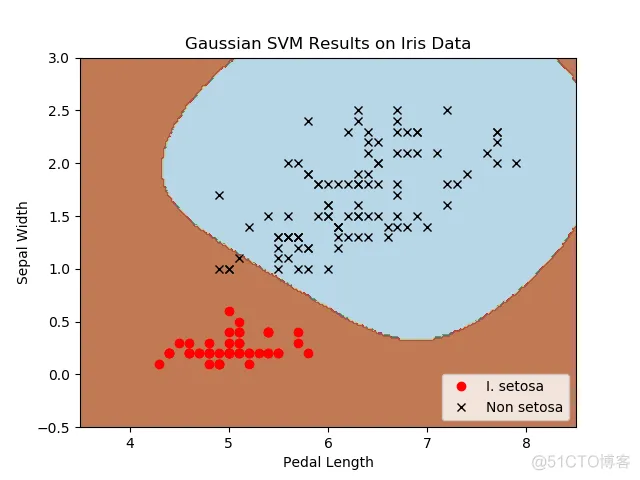
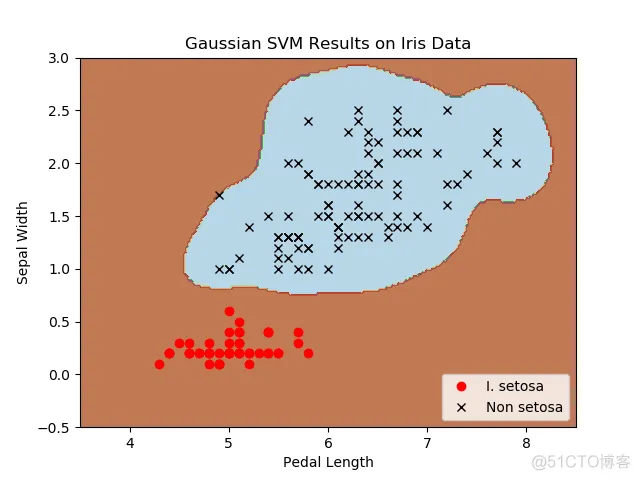
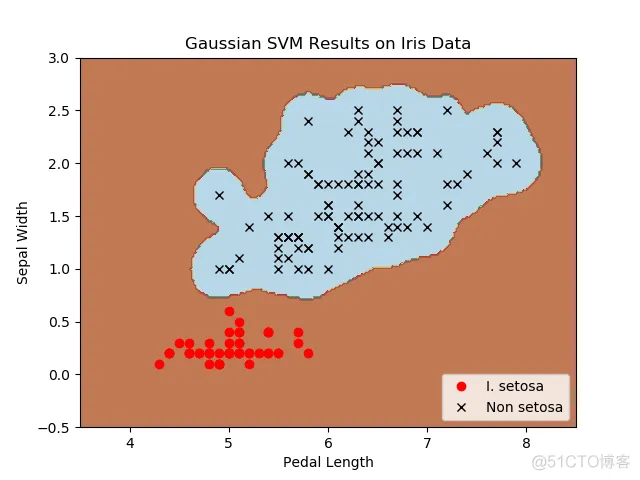
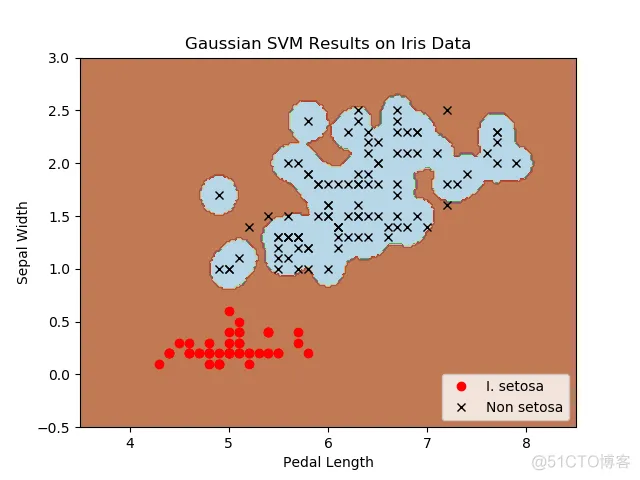
不同gamma值的山鸢尾花(I.setosa)的分类器结果图,采用高斯核函数的SVM。
gamma值越大,每个数据点对分类边界的影响就越大。
免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删