在多层感知器(Multilayer Perceptrons,简称MLP)中,每一层的神经元都连接到下一层的所有神经元。一般称这种类型的层为完全连接。
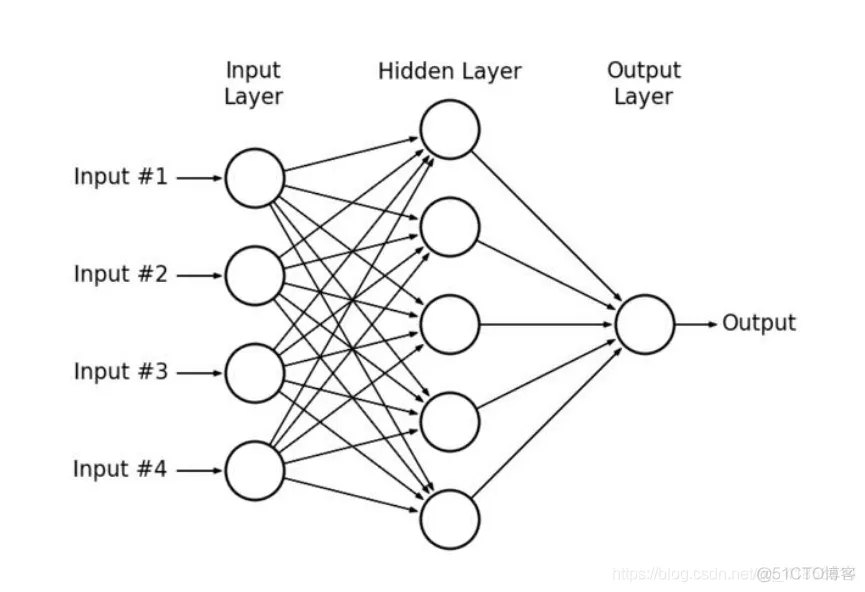
多层感知器示例
几个人站成一排第一个人看一幅画(输入数据),描述给第二个人(隐层)……依此类推,到最后一个人(输出)的时候,画出来的画肯定不能看了(误差较大)。反向传播就是,把画拿给最后一个人看(求取误差),然后最后一个人就会告诉前面的人下次描述时需要注意哪里(权值修正)
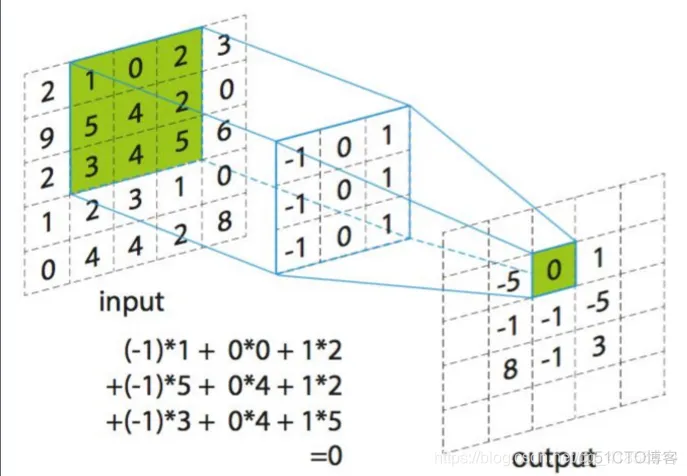
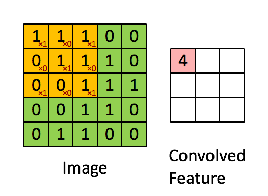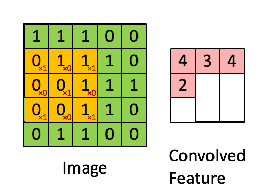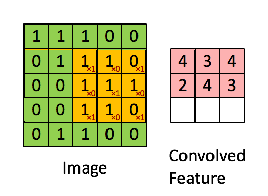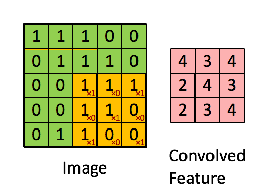
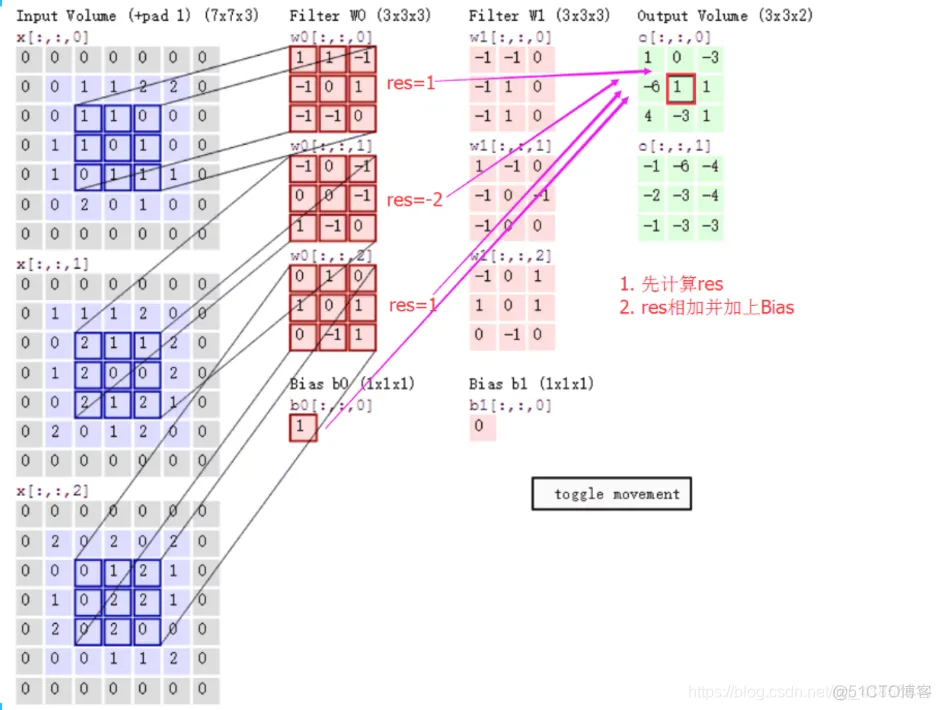
计算步骤解释如下,原图大小为7*7,通道数为3:,卷积核大小为3*3,Input Volume中的蓝色方框和Filter W0中红色方框的对应位置元素相乘再求和得到res(即,下图中的步骤1.res的计算),再把res和Bias b0进行相加(即,下图中的步骤2),得到最终的Output Volume
卷积示例
以下是一组未经过滤的猫咪照片:
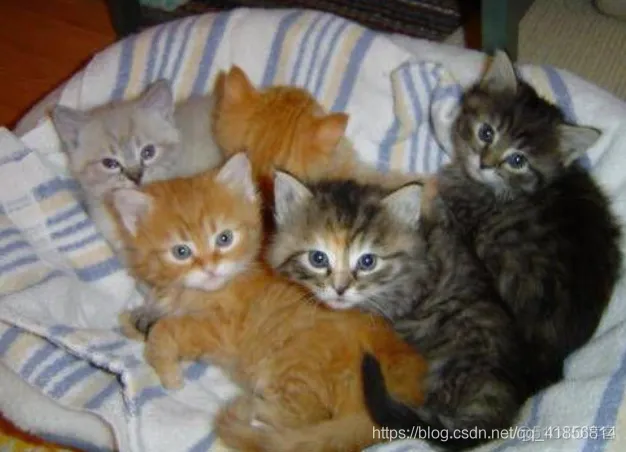

如果分别应用水平和垂直边缘滤波器,会得出以下结果:
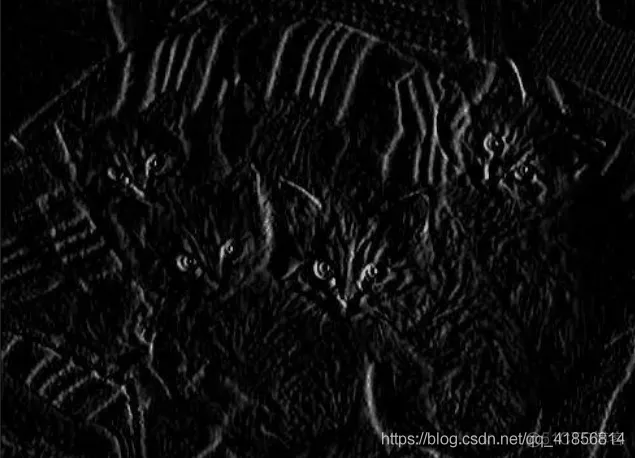

可以看到某些特征是变得更加显著的,而另一些特征逐渐消失。有趣的是,每个过滤器都展示了不同的特征。
这就是卷积神经网络学习识别图像特征的方法。
第一个参数:input [训练时一个batch图像的数量,图像高度,图像宽度, 图像通道数])
第二个参数:filter
filter就是卷积核(这里要求用Tensor来表示卷积核,并且Tensor(一个4维的Tensor,要求类型与input相同)的shape为[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]具体含义[卷积核高度,卷积核宽度,图像通道数,卷积核个数],这里的图片通道数也就input中的图像通道数,二者相同。)
第三个参数:strides
strides就是卷积操作时在图像每一维的步长,strides是一个长度为4的一维向量
第四个参数:padding
第五个参数:use_cudnn_on_gpu
第六个参数:data_format
NHWC:[batch, height, width, channels]
第七个参数:name
padding是一个string类型的变量,只能是 "SAME" 或者 "VALID",决定了两种不同的卷积方式。下面我们来介绍 "SAME" 和 "VALID" 的卷积方式,如下图我们使用单通道的图像,图像大小为5*5,卷积核用3*3
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_datafrom tensorflow.contrib.slim.python.slim.nets.inception_v3 import inception_v3_baseFLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGStf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("is_train", 1, "指定程序是预测还是训练")def full_connected(): # 获取真实的数据 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("./data/mnist/input_data/", one_hot=True) # 1、建立数据的占位符 x [None, 784] y_true [None, 10] with tf.variable_scope("data"): x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, 10]) # 2、建立一个全连接层的神经网络 w [784, 10] b [10] with tf.variable_scope("fc_model"): # 随机初始化权重和偏置 weight = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, 10], mean=0.0, stddev=1.0), name="w") bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[10])) # 预测None个样本的输出结果matrix [None, 784]* [784, 10] + [10] = [None, 10] y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias # 3、求出所有样本的损失,然后求平均值 with tf.variable_scope("soft_cross"): # 求平均交叉熵损失 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true, logits=y_predict)) # 4、梯度下降求出损失 with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"): train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) # 5、计算准确率 with tf.variable_scope("acc"): equal_list = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_true, 1), tf.argmax(y_predict, 1)) # equal_list None个样本 [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,..........] accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list, tf.float32)) # 收集变量 单个数字值收集 tf.summary.scalar("losses", loss) tf.summary.scalar("acc", accuracy) # 高纬度变量收集 tf.summary.histogram("weightes", weight) tf.summary.histogram("biases", bias) # 定义一个初始化变量的op init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 定义一个合并变量de op merged = tf.summary.merge_all() # 创建一个saver saver = tf.train.Saver() # 开启会话去训练 with tf.Session() as sess: # 初始化变量 sess.run(init_op) # 建立events文件,然后写入 filewriter = tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary/test/", graph=sess.graph) if FLAGS.is_train == 1: # 迭代步数去训练,更新参数预测 for i in range(2000): # 取出真实存在的特征值和目标值 mnist_x, mnist_y = mnist.train.next_batch(50) # 运行train_op训练 sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={x: mnist_x, y_true: mnist_y}) # 写入每步训练的值 summary = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x: mnist_x, y_true: mnist_y}) filewriter.add_summary(summary, i) print("训练第%d步,准确率为:%f" % (i, sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist_x, y_true: mnist_y}))) # 保存模型 saver.save(sess, "./tmp/ckpt/fc_model") else: # 加载模型 saver.restore(sess, "./tmp/ckpt/fc_model") # 如果是0,做出预测 for i in range(100): # 每次测试一张图片 [0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0] x_test, y_test = mnist.test.next_batch(1) print("第%d张图片,手写数字图片目标是:%d, 预测结果是:%d" % ( i, tf.argmax(y_test, 1).eval(), tf.argmax(sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test}), 1).eval() )) return None# 定义一个初始化权重的函数def weight_variables(shape): w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0)) return w# 定义一个初始化偏置的函数def bias_variables(shape): b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=shape)) return bdef model(): """ 自定义的卷积模型 :return: """ # 1、准备数据的占位符 x [None, 784] y_true [None, 10] with tf.variable_scope("data"): x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, 10]) # 2、一卷积层 卷积: 5*5*1,32个,strides=1 激活: tf.nn.relu 池化 with tf.variable_scope("conv1"): # 随机初始化权重, 偏置[32] w_conv1 = weight_variables([5, 5, 1, 32]) b_conv1 = bias_variables([32]) # 对x进行形状的改变[None, 784] [None, 28, 28, 1] x_reshape = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) # [None, 28, 28, 1]-----> [None, 28, 28, 32] x_relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(x_reshape, w_conv1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + b_conv1) # 池化 2*2 ,strides2 [None, 28, 28, 32]---->[None, 14, 14, 32] x_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(x_relu1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME") # 3、二卷积层卷积: 5*5*32,64个filter,strides=1 激活: tf.nn.relu 池化: with tf.variable_scope("conv2"): # 随机初始化权重, 权重:[5, 5, 32, 64] 偏置[64] w_conv2 = weight_variables([5, 5, 32, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variables([64]) # 卷积,激活,池化计算 # [None, 14, 14, 32]-----> [None, 14, 14, 64] x_relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(x_pool1, w_conv2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + b_conv2) # 池化 2*2, strides 2, [None, 14, 14, 64]---->[None, 7, 7, 64] x_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(x_relu2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME") # 4、全连接层 [None, 7, 7, 64]--->[None, 7*7*64]*[7*7*64, 10]+ [10] =[None, 10] with tf.variable_scope("conv2"): # 随机初始化权重和偏置 w_fc = weight_variables([7 * 7 * 64, 10]) b_fc = bias_variables([10]) # 修改形状 [None, 7, 7, 64] --->None, 7*7*64] x_fc_reshape = tf.reshape(x_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) # 进行矩阵运算得出每个样本的10个结果 y_predict = tf.matmul(x_fc_reshape, w_fc) + b_fc return x, y_true, y_predictdef conv_fc(): # 获取真实的数据 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("./data/mnist/input_data/", one_hot=True) # 定义模型,得出输出 x, y_true, y_predict = model() # 进行交叉熵损失计算 # 3、求出所有样本的损失,然后求平均值 with tf.variable_scope("soft_cross"): # 求平均交叉熵损失# 求平均交叉熵损失 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true, logits=y_predict)) # 4、梯度下降求出损失 with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"): train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(loss) # 5、计算准确率 with tf.variable_scope("acc"): equal_list = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_true, 1), tf.argmax(y_predict, 1)) # equal_list None个样本 [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,..........] accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list, tf.float32)) # 定义一个初始化变量的op init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 开启回话运行 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) # 循环去训练 for i in range(1000): # 取出真实存在的特征值和目标值 mnist_x, mnist_y = mnist.train.next_batch(50) # 运行train_op训练 sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={x: mnist_x, y_true: mnist_y}) print("训练第%d步,准确率为:%f" % (i, sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist_x, y_true: mnist_y}))) return Noneif __name__ == "__main__": conv_fc()1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.114.115.116.117.118.119.120.121.122.123.124.125.126.127.128.129.130.131.132.133.134.135.136.137.138.139.140.141.142.143.144.145.146.147.148.149.150.151.152.153.154.155.156.157.158.159.160.161.162.163.164.165.166.167.168.169.170.171.172.173.174.175.176.177.178.179.180.181.182.183.184.185.186.187.188.189.190.191.192.193.194.195.196.197.198.199.200.201.202.203.204.205.206.207.208.209.210.211.212.213.214.215.216.217.218.219.220.221.222.223.224.225.226.227.228.229.230.231.232.
.png)
代码:
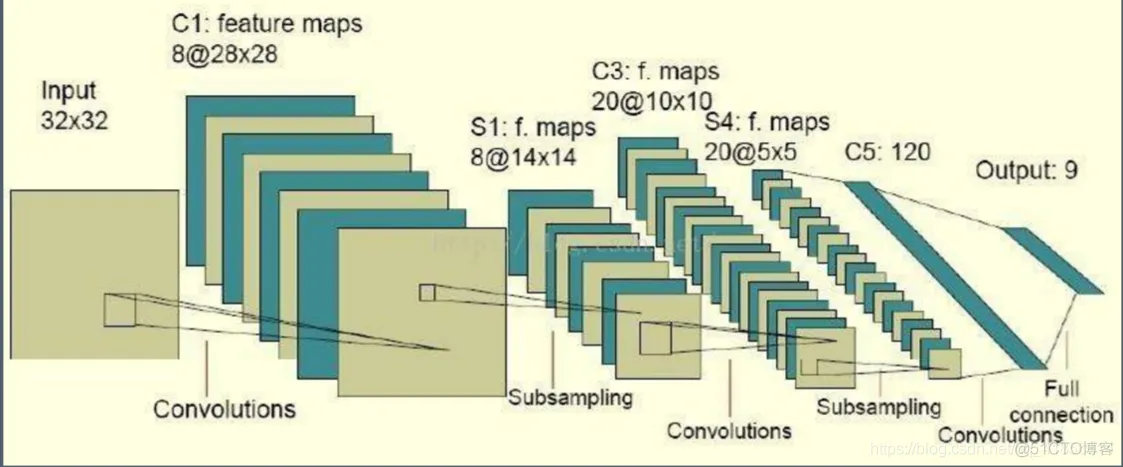
import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tfinput_ = np.random.randn(1,32,32,1).
astype('float32')filter_ = np.random.randn(5,5,1,8)
.astype('float32')conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_,filter_,[1,1,1,1],'VALID')conv1 = tf
.nn.relu(conv1)# 池化pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1,[1,2,2,1],[1,2,2,1],'SAME')
#第二层卷积filter2_ = np.random.randn(5,5,8,20)
.astype('float32')conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,filter2_,[1,1,1,1],'VALID')
#第二层池化pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2,[1,2,2,1],[1,2,2,1],'SAME')
#第三层卷积filter3_ = np.random.randn(5,5,20,120)
.astype('float32')conv3 = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2,filter3_,[1,1,1,1],'VALID')
#全连接层full = tf.reshape(conv3,shape = (1,120))W = tf
.random_normal(shape = [120,9])fc = tf
.matmul(full,W)fcnd = np.random.randn(30)tf.nn.relu(nd)with tf.Session()
as sess: ret =sess.run(tf.nn.relu(nd))
print(ret)1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.
31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.
免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删