产品
import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plttf.compat.v1
.disable_eager_execution()#3-1非线性回归#使用numpy生成200个随机点,200行1列x_data=np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200)
[:,np.newaxis]noise=np.random.normal(0,0.02,x_data.shape)#square为平方y_data=np
.square(x_data)+noiseprint(x_data)print(y_data)print(y_data.shape)#定义两个placeholder
#输入层:一个神经元x=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])y=tf.compat.v1
.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])#定义神经网络中间层#中间层:10个神经元Weights_L1=tf
.Variable(tf.compat.v1.random_normal([1,10]))biases_L1=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10]))Wx_plus_b_L1=tf
.matmul(x,Weights_L1)+biases_L1#L1中间层的输出,tanh为激活函数L1=tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L1)
#定义神经网络输出层#输出层:一个神经元Weights_L2=tf.Variable(tf.compat.v1.random_normal([10,1]))biases_L2=tf
.Variable(tf.zeros([1,1]))#输出层的输入就是中间层的输出,故为L1Wx_plus_b_L2=tf.matmul(L1,Weights_L2)+biases_L2
#预测结果prediction=tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L2)#二次代价函数#真实值减去预测值的平方的平均值loss=tf
.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))#梯度下降:学习率,最下化为losstrain_step=tf.compat.v1
.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)#定义会话with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
# 变量初始化 sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer())
# 开始训练 for _ in range(2000): #使用placeholder进行传值,传入样本值
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:x_data,y:y_data}) #训练好后,获得预测值,同时传入样本参数
prediction_value=sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={x:x_data}) #画图 plt.figure()
# 用散点图,来画出样本点 plt.scatter(x_data,y_data) # 预测图,红色实现,线款为5
plt.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw=5) plt.show()1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.
20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.
55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.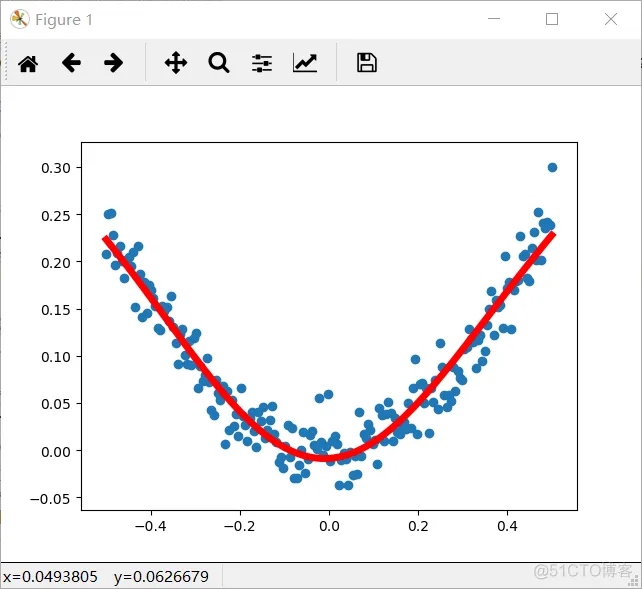
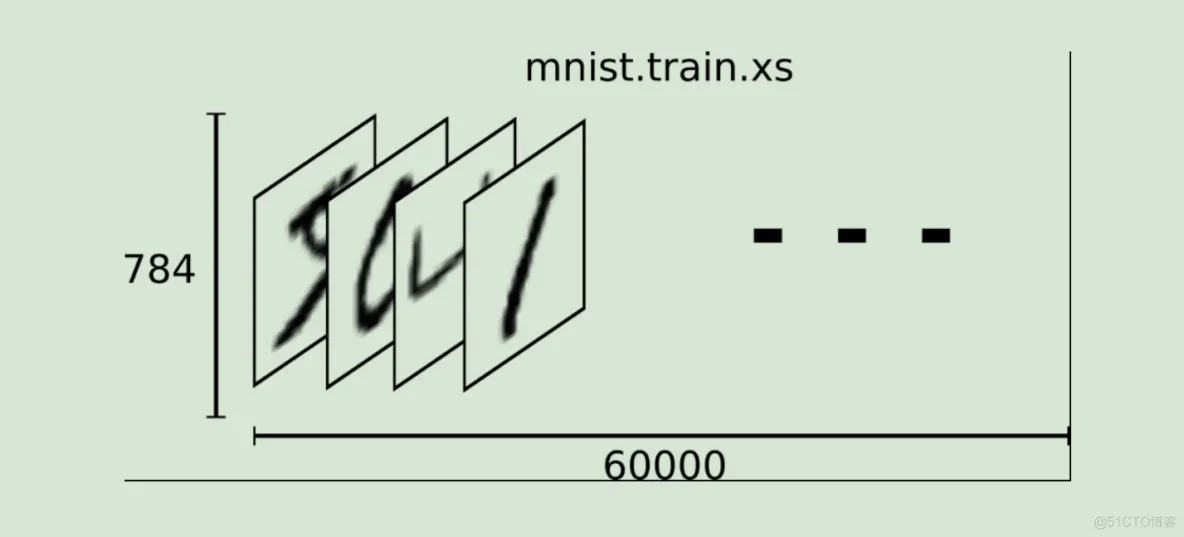
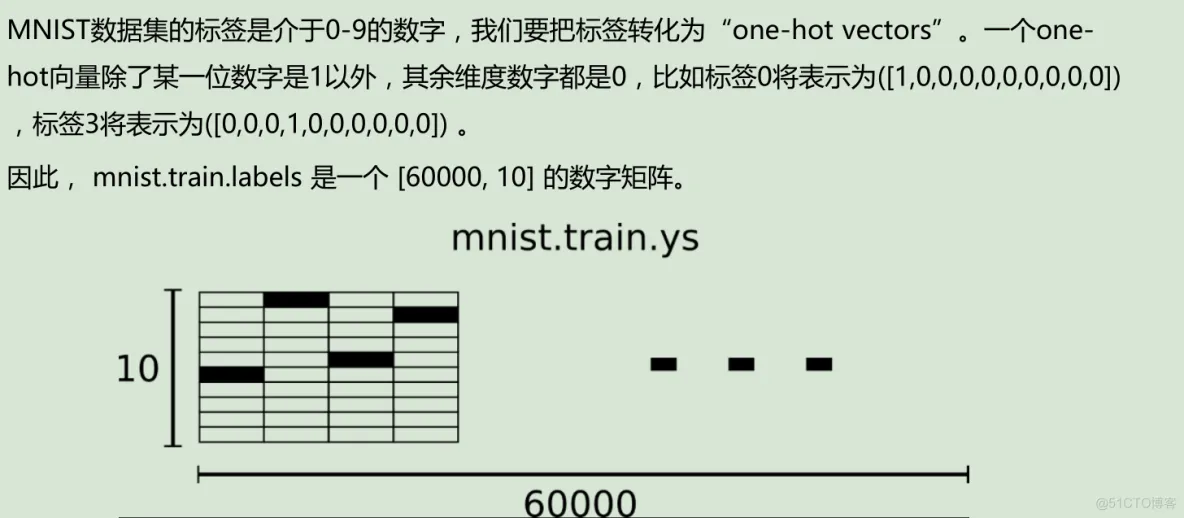
MNIST数据集的官网: Yann LeCun's website下载下来的数据集被分成两部分:60000行的训练数据集(mnist.train)和10000行的测试数据集(mnist.test)
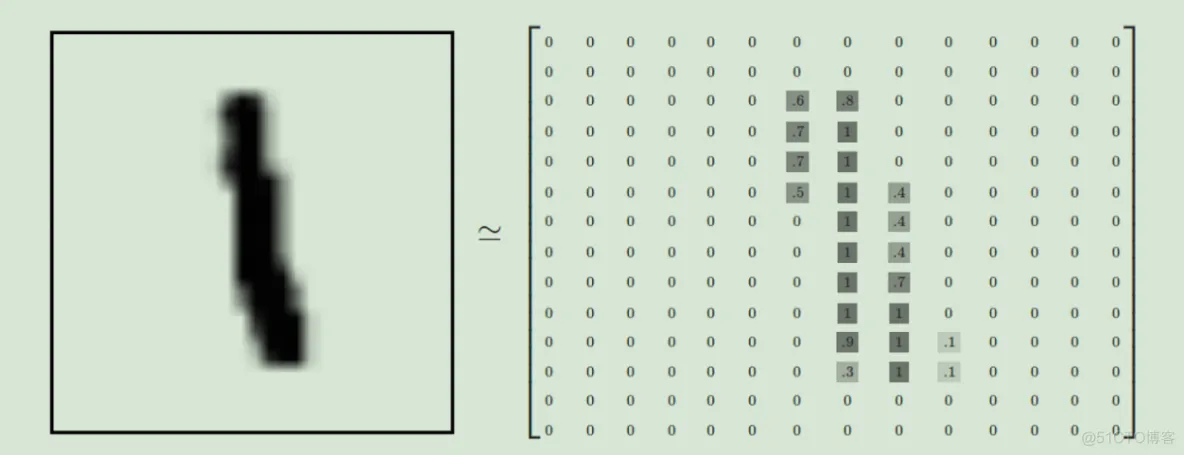
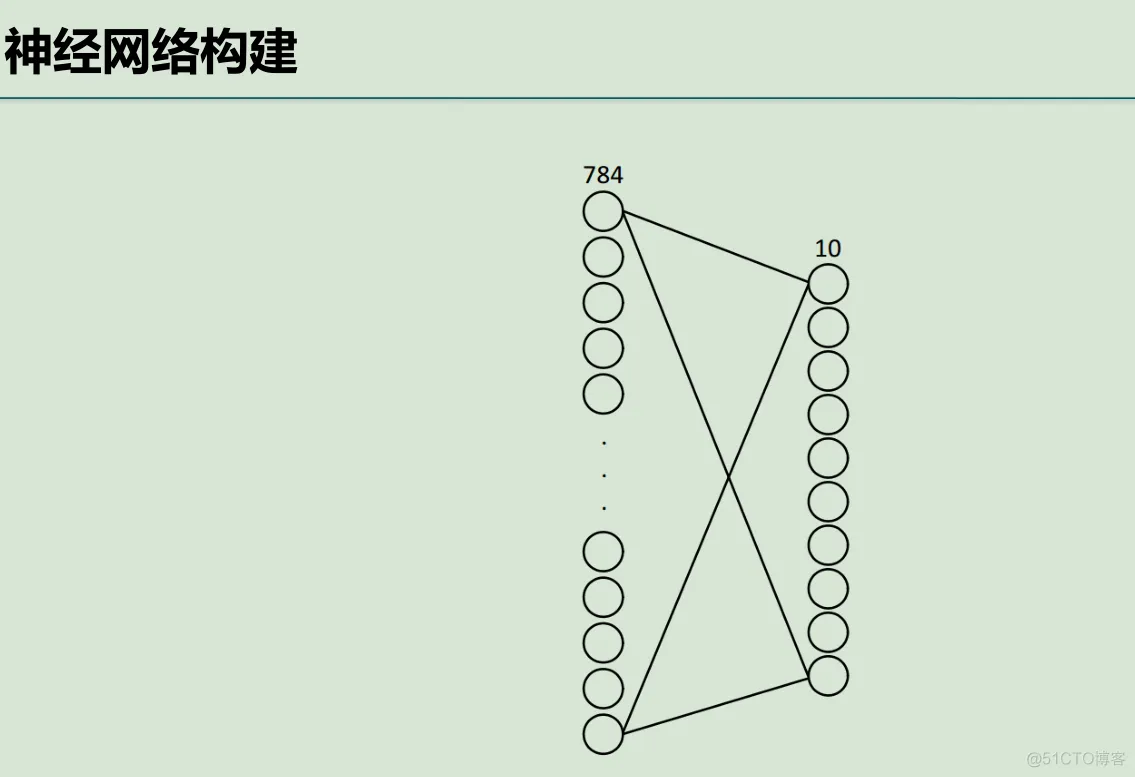
每一张图片包含28*28个像素,我们把这一个数组展开成一个向量,长度是28*28=784。因此在MNIST训练数据集中mnist.train.images 是一个形状为 [60000, 784] 的张量,第一个维度数字用来索引图片,第二个维度数字用来索引每张图片中的像素点。图片里的某个像素的强度值介于0-1之间。
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_datatf.compat
.v1.disable_eager_execution()import numpy as np#载入数据集mnist=input_data
.read_data_sets("MNIST_data",one_hot=True)#每个批次大小batch_size=100#计算一共有多少个批次n_bath=mnist
.train.num_examples // batch_sizeprint(n_bath)#定义两个placeholderx=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,
[None,784])y=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])#创建一个简单的神经网络W=tf
.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))prediction=tf.nn.softmax(tf
.matmul(x,W)+b)#二次代价函数loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))#梯度下降train_step=tf
.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)#初始化变量init=tf.compat
.v1.global_variables_initializer()#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中#返回的是一系列的True或False
argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置,对比两个最大位置是否一致correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf
.argmax(prediction,1))#求准确率#cast:将布尔类型转换为float,将True为1.0,False为0,然后求平均值accuracy=tf
.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init) for epoch in range(21): for batch in range(n_bath):
#获得一批次的数据,batch_xs为图片,batch_ys为图片标签
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
#进行训练 sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
#训练完一遍后,测试下准确率的变化
acc=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
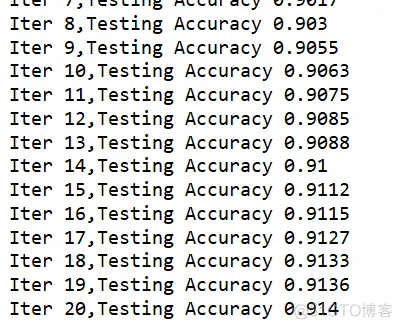
print("Iter "+str(epoch)+",Testing Accuracy "+str(acc))1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19
.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.输出:
优化方面:
①批次个数减小到20
②权值不再为0,改为随机数,设置参数要尽可能小
③增加一个隐藏层,节点数是sqrt(n*l),其中n是输入节点数,l是输出节点数,故为89
④代价函数更换为:交叉熵
⑤梯度下降函数更换为-->动量随机梯度下降,如果上次的准确率比这次准确率还要大,则将0.2乘以0.5
代码:
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_datatf.compat
.v1.disable_eager_execution()import numpy as np#载入数据集mnist=input_data
.read_data_sets("MNIST_data",one_hot=True)#每个批次大小batch_size=20#计算一共有多少个批次n_bath=mnist
.train.num_examples // batch_sizeprint(n_bath)#定义两个placeholderx=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf
.float32,[None,784])y=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])#创建一个简单的神经网络
#1.初始化非常重要,参数要尽可能小W=tf.Variable(tf.compat.v1.random_normal([784,89])/np.sqrt(784))b=tf
.Variable(tf.zeros([89]))prediction=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x,W)+b)#第二层
#2.我增加了一个神经网络层,节点数是sqrt(n*l),其中n是输入节点数,l是输出节点数W2=tf.Variable(tf.compat.v1
.random_normal([89,10])/np.sqrt(89))b2=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
#将其转换为概率值prediction2=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(prediction,W2)+b2)
#二次代价函数# loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction2))
#交叉熵loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction2))
#动量随机梯度下降#3.如果上次的准确率比这次准确率还要大,则将0.2乘以0.5train_step=tf.compat.v1.train
.MomentumOptimizer(0.2,0.5).minimize(loss)#初始化变量init=tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中#返回的是一系列的True或False argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置,
对比两个最大位置是否一致correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction2,1))
#求准确率#cast:将布尔类型转换为float,将True为1.0,False为0,然后求平均值accuracy=tf
.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: sess
.run(init) for epoch in range(21): for batch in range(n_bath):
#获得一批次的数据,batch_xs为图片,batch_ys为图片标签
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
#进行训练 sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
#训练完一遍后,测试下准确率的变化
acc=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
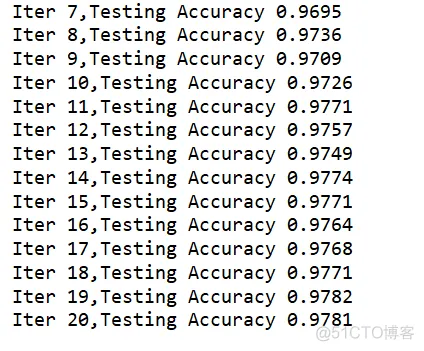
print("Iter "+str(epoch)+",Testing Accuracy "+str(acc))1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.
19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.
53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.输出:
免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删