ANSYS中重力载荷的施加方法
1. 按照加速度载荷处理:Acceleration 与重力方向相反
2. 添加标准重力载荷:Standard Earth Gravity 与重力方向相同
以下解释均来自于ANSYS官方帮助文档:
Acceleration
The global Acceleration boundary condition defines a linear acceleration of a structure in each of the global Cartesian axis directions.
全局加速度边界条件定义了结构在每一个全局笛卡尔轴方向上的线性加速度。
If desired, acceleration can be used to simulate gravity (by using inertial effects) by accelerating a structure in the direction opposite of gravity (the natural phenomenon of). That is, accelerating a structure vertically upwards (+Y) at 9.80665 m/s2(in metric units), applies a force on the structure in the opposite direction (-Y) inducing gravity (pushing the structure back towards earth). Units are length/time2.
如果需要,加速度可以用来模拟重力(通过使用惯性效应),在与重力(的自然现象)相反的方向加速一个结构。也就是说,以9.80665 m/s2(公制单位)的速度垂直向上加速结构(+Y),在结构上施加一个相反方向的力(-Y),产生重力(将结构推回地球)。单位是length/time2。
Alternatively, you can use the Standard Earth Gravity load to produce the effect of gravity. Gravity and Acceleration are essentially the same type of load except they have opposite sign conventions and gravity has a fixed magnitude. For applied gravity, a body tends to move in the direction of gravity and for applied acceleration, a body tends to move in the direction opposite of the acceleration.
或者,您可以使用标准地球重力负载来产生重力的效果。重力和加速度本质上是相同类型的载荷,除了它们有相反的符号约定和重力有固定的大小。对于施加的重力,物体倾向于向重力的方向移动;对于施加的加速度,物体倾向于向加速度的相反方向移动。
Standard Earth Gravity
This boundary condition simulates gravitational effects on a body in the form of an external force.
此边界条件以外力的形式模拟了物体上的重力效应。
Gravity is a specific example of acceleration with an opposite sign convention and a fixed magnitude. Gravity loads cause a body to move in the direction of gravity. Acceleration loads cause a body to move in the direction opposite of the acceleration.
重力是加速度的一个特殊例子,具有相反的符号约定和固定的大小。重力荷载使物体沿重力方向运动。加速度载荷使物体向与加速度相反的方向运动。
Loading Data Definition: Standard Earth Gravity is constant, only the direction may be modified.
两种施加方法对比
下面的插图比较了如何使用Acceleration and Standard Earth Gravity(加速度和重力)来指定具有相同结果的重力负载。
Acceleration Example
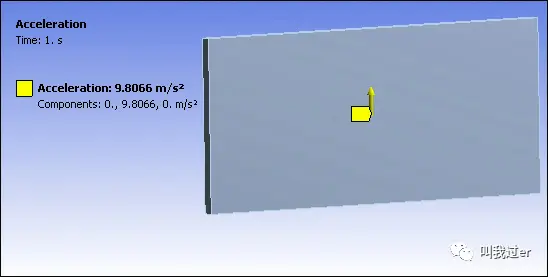
Global Acceleration load applied in the +tyY direction to simulate gravi
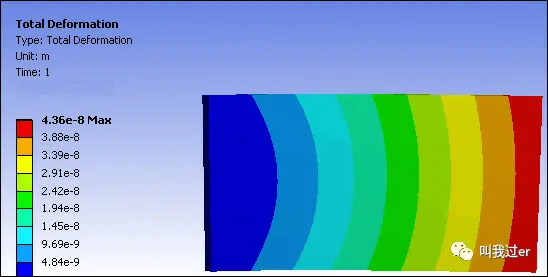
Resulting deformation
Standard Earth Gravity Example
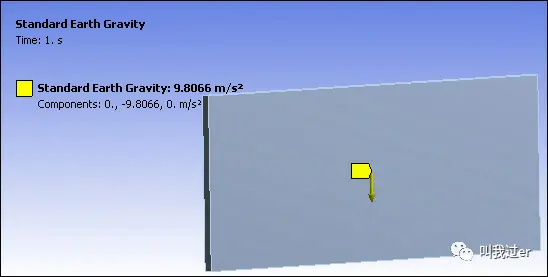
Standard Earth Gravity applied
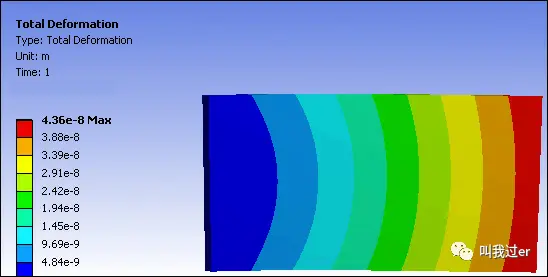
Resulting deformation
Tips:
惯性力是指:当物体有加速度时(可以是加速阶段,也可以是减速阶段)时,物体具有的惯性会使物体有保持原有运动状态的倾向,而此时若以该物体为参考系,并在该参考系上建立坐标系,看起来就仿佛有一股方向相反的力作用在该物体上令该物体在坐标系内发生位移,因此称之为惯性力。
因为惯性力实际上并不存在,实际存在的只有原本将该物体加速的力,因此惯性力又称为假想力。它概念的提出是因为在非惯性系中,牛顿运动定律并不适用。但是为了思维上的方便,可以假想在这个非惯性系中,除了相互作用所引起的力之外还受到一种由于非惯性系而引起的力——惯性力。
参考文献:ansys帮助文档
武汉格发信息技术有限公司,格发许可优化管理系统可以帮你评估贵公司软件许可的真实需求,再低成本合规性管理软件许可,帮助贵司提高软件投资回报率,为软件采购、使用提供科学决策依据。支持的软件有: CAD,CAE,PDM,PLM,Catia,Ugnx, AutoCAD, Pro/E, Solidworks ,Hyperworks, Protel,CAXA,OpenWorks LandMark,MATLAB,Enovia,Winchill,TeamCenter,MathCAD,Ansys, Abaqus,ls-dyna, Fluent, MSC,Bentley,License,UG,ug,catia,Dassault Systèmes,AutoDesk,Altair,autocad,PTC,SolidWorks,Ansys,Siemens PLM Software,Paradigm,Mathworks,Borland,AVEVA,ESRI,hP,Solibri,Progman,Leica,Cadence,IBM,SIMULIA,Citrix,Sybase,Schlumberger,MSC Products...