总分 = 德育分 * 60% + 智育分 * 60% + 体育分 * 60%
假设家长不知道这个规则,已知:
经过家长们的分析,只有三项分数各自乘以的权重系数是未知的。问题演变成求解方程:w1x + w2y + w3z = A 中的三个 w 即权重。其中 x、y、z、A 分别对应几位学生的德育分、智育分、体育分和总分。
两个方程式解三个未知数无法求解:
90w1 + 80w2 + 70w3 = 85
98w1 + 95w2 + 87w3 = 96
神经网络模型图的一般约定:
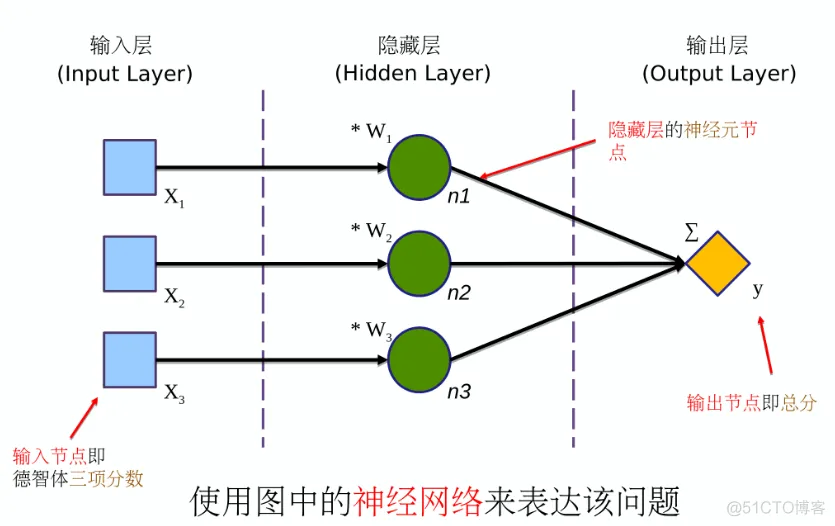
神经网络的代码:
import tensorflow as tf
x1 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x2 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x3 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
w1 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
w2 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
w3 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
n1 = x1 * w1
n2 = x2 * w2
n3 = x3 * w3
y = n1 + n2 + n3
sess = tf.Session()
init = tf.global_variable_initializer()
sess.run(init)
result = sess.run([x1, x2, x3, w1, w2, w3, y], feed_dict={x1: 90, x2: 80, x3: 70})
print(result)
x1 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x2 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x3 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
通过 tf.placeholder 定义三个占位符(placeholder),作为神经网络的输入节点,来准备分别接收德育、智育、体育三门分数作为神经网络的输入。dtype 是 data type 的缩写,dtype = tf.float3 是命令参数,tf.float32 代表 32 位小数。
w1 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
w2 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
w3 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
通过 tf.Variable() 定义三个可变参数。
n1 = x1 * w1
n2 = x2 * w2
n3 = x3 * w3
n1、n2、n3 是三个隐藏层节点,实际上是他们的计算算式。
y = n1 + n2 + n3
定义输出节点 y,也就是总分的计算公式(加权求和)。至此,神经网络模型的定义完成。
sess = tf.Session()
定义神经网络的会话对象
init = tf.global_variable_initializer()
tf.global_variable_initializer() 返回专门用于初始化可变参数的对象。
sess.run(init)
初始化所有的可变参数。
result = sess.run([x1, x2, x3, w1, w2, w3, y], feed_dict={x1: 90, x2: 80, x3: 70})
print(result)
[x1, x2, x3, w1, w2, w3, y] 为要查看的结果项,feed_dict={x1: 90, x2: 80, x3: 70} 为输入的数据。输入三门分数运行神经网络并获得该神经网络输出的节点值。
运行代码,查看结果:
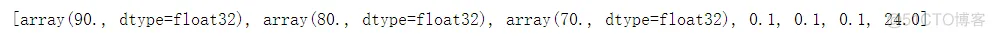
根据随意设置的可变参数初始值计算出的输出结果正确,证明搭建的神经网络可以运行,但不能真正投入使用,存在一定误差。
如果你使用了 TensorFlow 2.x 上述代码中可能存在兼容问题,但是可以通过更改部分代码解决:
代码
# import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
x1 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x2 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x3 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
w1 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
w2 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
w3 = tf.Variable(0.1, dtype = tf.float32)
n1 = x1 * w1
n2 = x2 * w2
n3 = x3 * w3
y = n1 + n2 + n3
sess = tf.Session()
# init = tf.global_variable_initializer()
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
result = sess.run([x1, x2, x3, w1, w2, w3, y], feed_dict={x1: 90, x2: 80, x3: 70})
print(result)
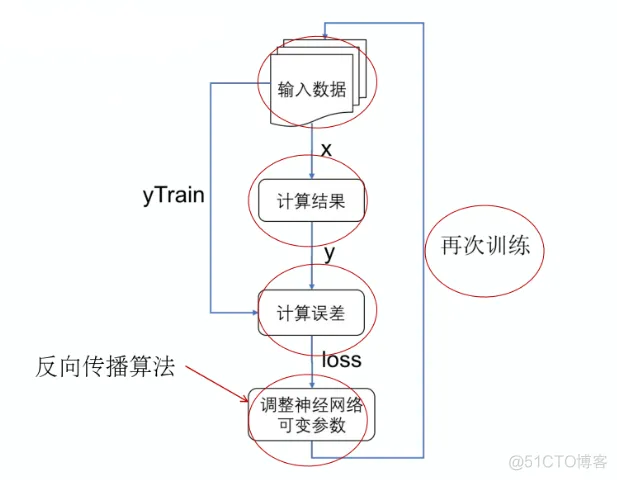
神经网络在投入使用前,都要经过训练(train)的过程才能有准确的输出。
x1 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x2 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
x3 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
yTrain = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
给神经网络增加一个输入项 —— 目标值 yTrain,用来表示正确的总分结果。增加误差函数 loss,优化器 optimizer 和训练对象 train。
y = n1 + n2 + n3
loss = tf.abs(y - yTrain)
optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(0.001)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
tf.abs 函数用于取绝对值:计算结果 y 与目标值 yTrain 之间的误差。使用 RMSProp 优化器其中参数是学习率。optimizer.minimize 让优化器按照把 loss 最小化的原则来调整可变参数。
“误差函数”(又叫损失函数)用于让神经网络来判断当前网络的计算结果与目标值(也就是标准答案)相差多少。“训练对象”被神经网络用于控制训练的方式,常见的训练的方式是设法使误差函数的计算值越来越小。
免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删