产品
前言
学习API前,我希望你们是已经接触过相关编程语言的学习(以下内容为C#的编程环境)
对象拓扑图:
SOLIDWORKS API 的操作可以理解为是:在获取不同对象后,进行对象的方法()操作和对象属性读写{get,set}的过程。那我我们的关键就是学会API的接口对象的获得。如下我找了一张其对象关系拓扑图:
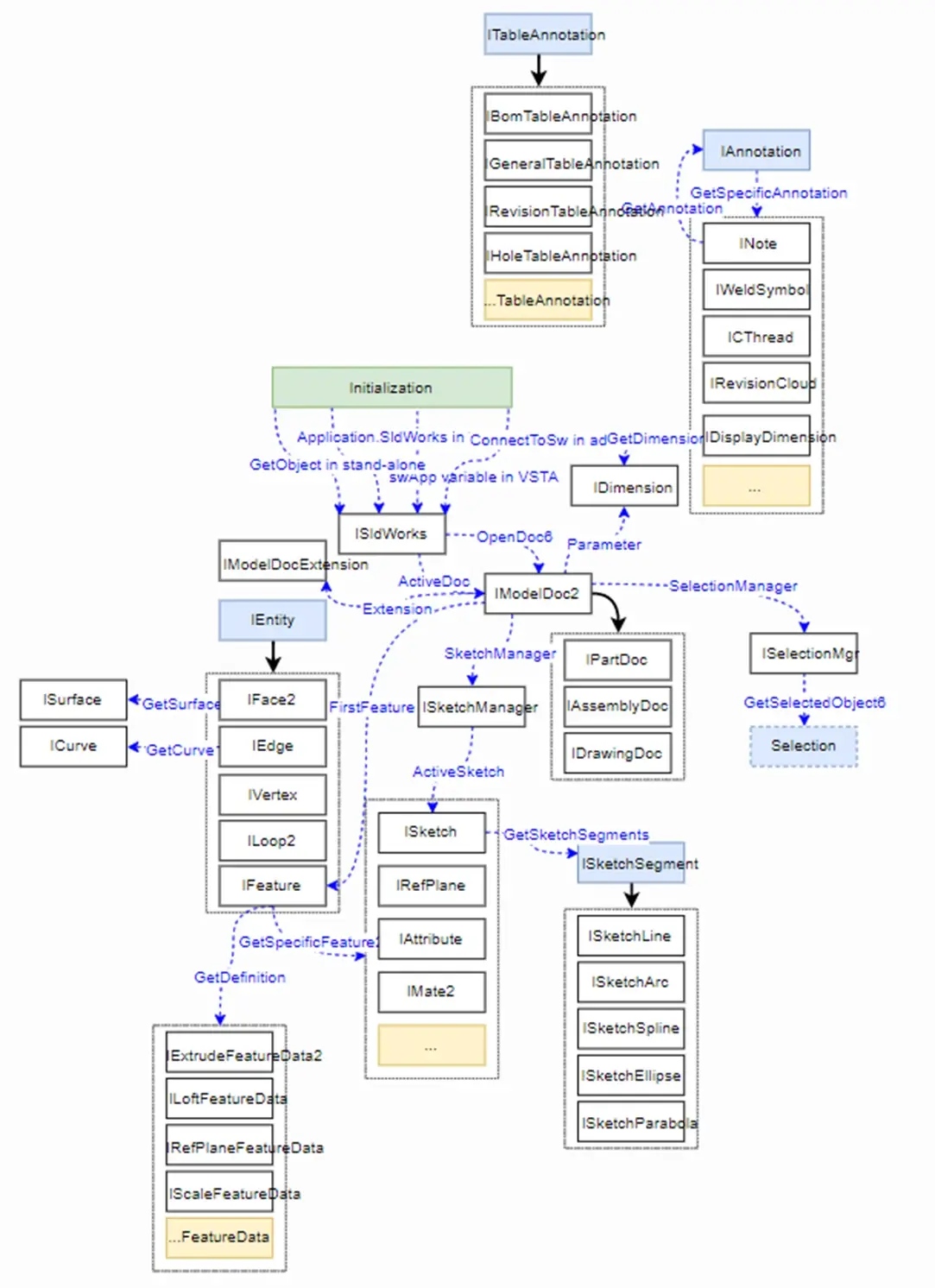
API对象关系拓扑图
获得程序(ISldWorks)
SldWorks swApp
//如果是安装单个版本的SW时
swApp = (SldWorks)Marshal.GetActiveObject("SldWorks.Application");
//如果是有多个版本的SW时,可能需要区分:
swApp = (SldWorks)Marshal.GetActiveObject("SldWorks.Application.26");//2018
swApp = (SldWorks)Marshal.GetActiveObject("SldWorks.Application.27");//2019
swApp = (SldWorks)Marshal.GetActiveObject("SldWorks.Application.28");//2020……获得文件
string filename = @"C:\WINDOWS\Temp\xxx.sldprt";
//打开方式 OpenDoc(文件路径,文件类型)
swApp.OpenDoc(filename, (int)swDocumentTypes_e.swDocPART);
//激活当前文件:
PartDoc swPart = (AssemblyDoc)swApp.ActiveDoc; //类型1:零件
AssemblyDoc swAssy = (AssemblyDoc)swApp.ActiveDoc; //类型2:装配体
DrawingDoc swDraw = (AssemblyDoc)swApp.ActiveDoc; //类型3:工程图获得零部件
//打开装配体&获得当前装配体的零部件集合
public static string[] GetComps()
{
AssemblyDoc swAssy = (AssemblyDoc)swApp.ActiveDoc;
string[] Comppaths = (string[])swAssy.GetComponents(true);
return Comppaths;
}获得图纸
public static void GetSheetNames()
{
//获取当前工程图对象
Sheet drwSheet = (Sheet)swDraw.GetCurrentSheet();
//获取当前工程图中的所有图纸名称
object[] sheetNames = (object[])swDraw.GetSheetNames();
//获取当前工程图中的所有图纸视图
object[] views = (object[])drwSheet.GetViews();
//遍历工程图零部件,输入选择视图,输出零部件名
foreach (View view in views)
{
//选择视图激活
DrawingComponent comp = view.RootDrawingComponent; Debug.Print(comp.Name);
//获得子件对象
object[] childrencomps = (object[])comp.GetChildren();
//遍历工程图零部件
for (int i = childrencomps.GetLowerBound(0); i <= childrencomps.GetUpperBound(0); i++)
{
Debug.Print("零部件是" + ((DrawingComponent)childrencomps[i]).Name);
}
}
}获得特征
// 遍历特征对象,根据特征名称找到特征对象来操作。
public static void TraverseFeatures(bool isTopLevel)
{
//获得第一个特征,并赋值到当前特征curFeat
Feature thisFeat = (Feature)swDoc.FirstFeature();
Feature curFeat = default(Feature); curFeat = thisFeat;
//当前特征非空就继续输出特征信息
while ((curFeat != null))
{
/*——————/
特征操作
/——————*/
//进入下一个特征
Feature nextFeat = default(Feature);
if (isTopLevel) { nextFeat = (Feature)curFeat.GetNextFeature(); }
else { nextFeat = null; }
curFeat = nextFeat; nextFeat = null;
}
}获得属性(CustomPropertyManager)
string PropertyName;//定义属性名
string PropertyValue;//定义属性值
//获得自定义属性对象(配置属性在双引号填[“配置名称”])
CustomPropertyManager cusPropMgr = swDoc.Extension.CustomPropertyManager[""];
//获得属性:GetAll获得自定义属性内容,将obj转属性名数组
cusPropMgr.GetAll2(ref vPropNamesObject, ref vPropTypes, ref vPropValues, swCustomInfoGetResult_e.swCustomInfoGetResult_NotPresent);
object[] vPropNames = (object[])vPropNamesObject; if (vPropNames == null) { return; }
//增加属性:Add(属性名,类型,属性值,添加时的设置)
cusPropMgr.Add3(PropertyName, (int)swCustomInfoType_e.swCustomInfoText, PropertyValue, (int)swCustomPropertyAddOption_e.swCustomPropertyDeleteAndAdd);
//修改属性:
vPropNames[i]=”修改后的属性值”
//删除属性:
cusPropMgr.Delete2(PropertyName);
补充:
dynamic IAssemblyDoc.GetComponents(bool ToplevelOnly);
通常用object[]接受,可在实际使用时转其他可用类型,常见转string[]。