人脸姿态估计主要是获得脸部朝向的角度信息。一般可以用旋转矩阵、旋转向量、四元数或欧拉角表示(这四个量也可以互相转换)。一般而言,欧拉角可读性更好一些,使用更为广泛。本文获得的人脸姿态信息用三个欧拉角(pitch,yaw,roll)表示。
欧拉角动图注解
pitch:俯仰角,表示物体绕x轴旋转

yaw:偏航角,表示物体绕y轴旋转
roll:翻滚角,表示物体绕z轴旋转
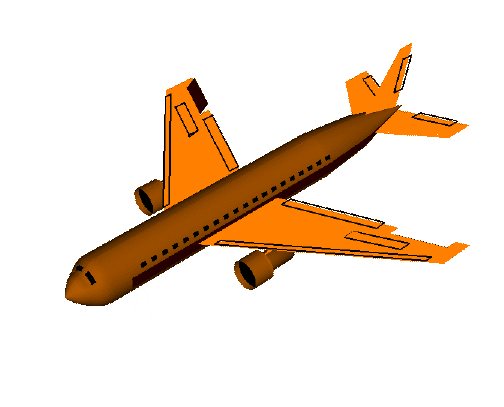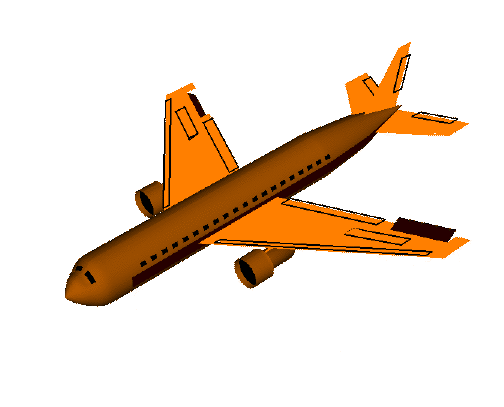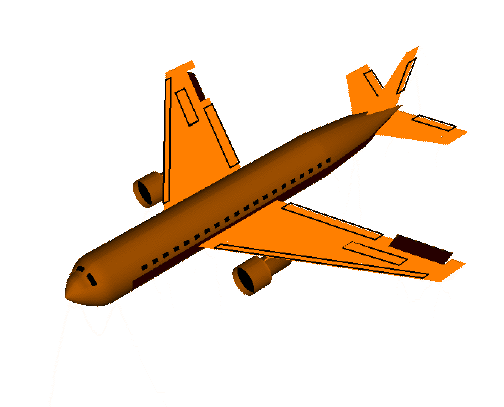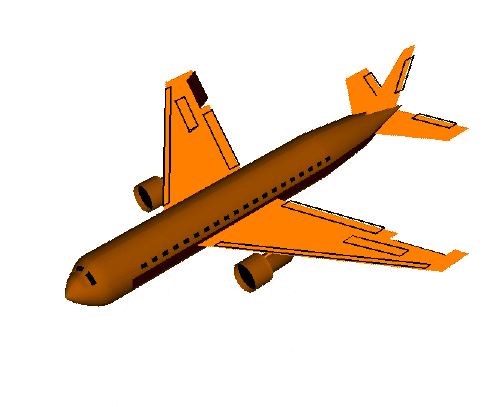
1)首先定义一个具有n个关键点的3D脸部模型,n可以根据自己对准确度的容忍程度进行定义,以下示例定义6个关键点的3D脸部模型(左眼角,右眼角,鼻尖,左嘴角,右嘴角,下颌);
2)采用人脸检测以及面部关键点检测得到上述3D脸部对应的2D人脸关键点;
3)采用Opencv的solvePnP函数解出旋转向量;
4)将旋转向量转换为欧拉角;
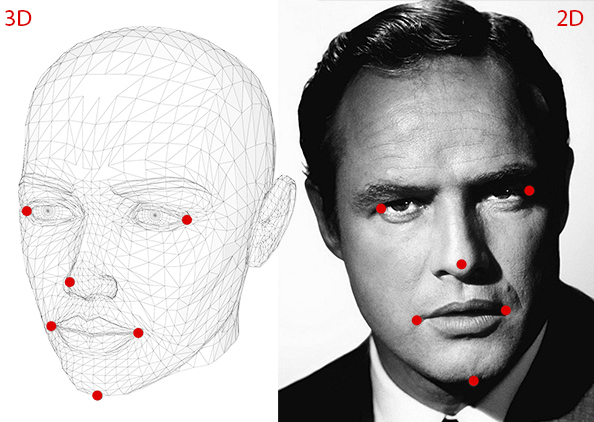
C++ // 3D model points. std::vector<cv::Point3d> model_points; model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)); // Nose tip model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(0.0f, -330.0f, -65.0f)); // Chin model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(-225.0f, 170.0f, -135.0f)); // Left eye left corner model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(225.0f, 170.0f, -135.0f)); // Right eye right corner model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(-150.0f, -150.0f, -125.0f)); // Left Mouth corner model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(150.0f, -150.0f, -125.0f)); // Right mouth corner python # 3D model points.model_points = np.array([ (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), # Nose tip (0.0, -330.0, -65.0), # Chin (-225.0, 170.0, -135.0), # Left eye left corner (225.0, 170.0, -135.0), # Right eye right corne (-150.0, -150.0, -125.0), # Left Mouth corner (150.0, -150.0, -125.0) # Right mouth corner ])利用相关算法进行人脸关键点检测,一般常见68个关键点检测模型,其具体顺序如下所示,而6个关键点对应的索引id分别为:
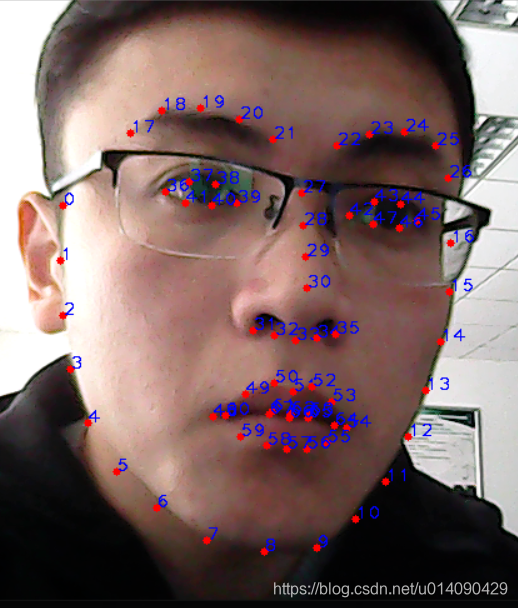
下巴:8
鼻尖:30
左眼角:36
右眼角:45
左嘴角:48
右嘴角:54
C++ // 2D image points. If you change the image, you need to change vector std::vector<cv::Point2d> image_points; image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(359, 391) ); // Nose tip image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(399, 561) ); // Chin image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(337, 297) ); // Left eye left corner image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(513, 301) ); // Right eye right corner image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(345, 465) ); // Left Mouth corner image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(453, 469) ); // Right mouth corner python #2D image points. If you change the image, you need to change vectorimage_points = np.array([ (359, 391), # Nose tip (399, 561), # Chin (337, 297), # Left eye left corner (513, 301), # Right eye right corne (345, 465), # Left Mouth corner (453, 469) # Right mouth corner ], dtype="double")OpenCV中solvePnP 和 solvePnPRansac都可以用来估计Pose。第二个solvePnPRansac利用随机抽样一致算法(Random sample consensus,RANSAC)的思想,虽然计算出的姿态更加精确,但速度慢、没法实现实时系统,所以我们这里只关注第一个solvePnP函数,具体的参数可以参见Opencv文档。
solvePnP implements several algorithms for pose estimation which can be selected using the parameter flag. By default it uses the flag SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE which is essentially the DLT solution followed by Levenberg-Marquardt optimization. SOLVEPNP_P3P uses only 3 points for calculating the pose and it should be used only when using solvePnPRansac. C++: bool solvePnP(InputArray objectPoints, InputArray imagePoints, InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs, OutputArray rvec, OutputArray tvec, bool useExtrinsicGuess=false, int flags=SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE )确定pose也就是确定从3D model到图片中人脸的仿射变换矩阵,它包含旋转和平移的信息。solvePnP函数输出结果包括旋转向量(roatation vector)和平移向量(translation vector)。这里我们只关心旋转信息,所以主要将对 roatation vector进行操作。
在调用solvePnP函数前需要初始化cameraMatrix,也就是相机内参,并调用solvePnP函数:
c++ // Camera internals double focal_length = im.cols; // Approximate focal length. cv::Point2d center = cv::Point2d(im.cols / 2, im.rows / 2); cv::Mat camera_matrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << focal_length, 0, center.x, 0, focal_length, center.y, 0, 0, 1); cv::Mat dist_coeffs = cv::Mat::zeros(4, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type); // Assuming no lens distortion cv::Mat rotation_vector; // Rotation in axis-angle form cv::Mat translation_vector; // Solve for pose cv::solvePnP(model_points, landmarks, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, rotation_vector, translation_vector); python # Camera internals focal_length = size[1]center = (size[1]/2, size[0]/2)camera_matrix = np.array( [[focal_length, 0, center[0]], [0, focal_length, center[1]], [0, 0, 1]], dtype = "double" ) print "Camera Matrix :\n {0}".format(camera_matrix) dist_coeffs = np.zeros((4,1)) # Assuming no lens distortion(success, rotation_vector, translation_vector) = cv2.solvePnP(model_points, image_points, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, flags=cv2.CV_ITERATIVE) print "Rotation Vector:\n {0}".format(rotation_vector)print "Translation Vector:\n {0}".format(translation_vector)旋转向量转旋转矩阵theta = np.linalg.norm(rvec)r = rvec / thetaR_ = np.array([[0, -r[2][0], r[1][0]], [r[2][0], 0, -r[0][0]], [-r[1][0], r[0][0], 0]])R = np.cos(theta) * np.eye(3) + (1 - np.cos(theta)) * r * r.T + np.sin(theta) * R_print('旋转矩阵')print(R)旋转矩阵转欧拉角def isRotationMatrix(R): Rt = np.transpose(R) #旋转矩阵R的转置 shouldBeIdentity = np.dot(Rt, R) #R的转置矩阵乘以R I = np.identity(3, dtype=R.dtype) # 3阶单位矩阵 n = np.linalg.norm(I - shouldBeIdentity) #np.linalg.norm默认求二范数 return n < 1e-6 # 目的是判断矩阵R是否正交矩阵(旋转矩阵按道理须为正交矩阵,如此其返回值理论为0) def rotationMatrixToAngles(R): assert (isRotationMatrix(R)) #判断是否是旋转矩阵(用到正交矩阵特性) sy = math.sqrt(R[0, 0] * R[0, 0] + R[1, 0] * R[1, 0]) #矩阵元素下标都从0开始(对应公式中是sqrt(r11*r11+r21*r21)),sy=sqrt(cosβ*cosβ) singular = sy < 1e-6 # 判断β是否为正负90° if not singular: #β不是正负90° x = math.atan2(R[2, 1], R[2, 2]) y = math.atan2(-R[2, 0], sy) z = math.atan2(R[1, 0], R[0, 0]) else: #β是正负90° x = math.atan2(-R[1, 2], R[1, 1]) y = math.atan2(-R[2, 0], sy) #当z=0时,此公式也OK,上面图片中的公式也是OK的 z = 0 x = x*180.0/3.141592653589793 y = y*180.0/3.141592653589793 z = z*180.0/3.141592653589793 return np.array([x, y, z])# 从旋转向量转换为欧拉角def get_euler_angle(rotation_vector): # calculate rotation angles theta = cv2.norm(rotation_vector, cv2.NORM_L2) # transformed to quaterniond w = math.cos(theta / 2) x = math.sin(theta / 2)*rotation_vector[0][0] / theta y = math.sin(theta / 2)*rotation_vector[1][0] / theta z = math.sin(theta / 2)*rotation_vector[2][0] / theta ysqr = y * y # pitch (x-axis rotation) t0 = 2.0 * (w * x + y * z) t1 = 1.0 - 2.0 * (x * x + ysqr) print('t0:{}, t1:{}'.format(t0, t1)) pitch = math.atan2(t0, t1) # yaw (y-axis rotation) t2 = 2.0 * (w * y - z * x) if t2 > 1.0: t2 = 1.0 if t2 < -1.0: t2 = -1.0 yaw = math.asin(t2) # roll (z-axis rotation) t3 = 2.0 * (w * z + x * y) t4 = 1.0 - 2.0 * (ysqr + z * z) roll = math.atan2(t3, t4) print('pitch:{}, yaw:{}, roll:{}'.format(pitch, yaw, roll)) # 单位转换:将弧度转换为度 Y = int((pitch/math.pi)*180) X = int((yaw/math.pi)*180) Z = int((roll/math.pi)*180) return 0, Y, X, ZPS:
人脸旋转的极限角度:
Pitch -60.4~69.6Yaw -79.8~75.3Roll -40.9~63.3误差范围:
Pitch: 5.10Yaw: 4.20Roll: 2.40免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删