产品
MATLAB2021a
% CHANNEL EQUALIZATION USING LMS clc;clear all;close all;M=3000; % number of data samplesT=2000;
% number of training symbolsdB=25; % SNR in dB valueL=20; % length for smoothing(L+1)ChL=5;
% length of the channel(ChL+1)EqD=round((L+ChL)/2); %delay for equalizationCh=randn(1,ChL+1)+sqrt(-1)*
randn(1,ChL+1); % complex channelCh=Ch/norm(Ch);
% scale the channel with normTxS=round(rand(1,M))*2-1;
% QPSK transmitted sequenceTxS=TxS+sqrt(-1)*(round(rand(1,M))*2-1);x=filter(Ch,1,TxS);
%channel distortionn=randn(1,M); %+sqrt(-1)*randn(1,M);
%Additive white gaussian noise n=n/norm(n)*10^(-dB/20)*norm(x);
% scale the noise power in accordance with SNRx=x+n;
% received noisy signalK=M-L;
%% Discarding several starting samples for avoiding 0's and negativeX=zeros(L+1,K);
% each vector column is a samplefor i=1:K X(:,i)=x(i+L:-1:i).';
end%adaptive LMS Equalizere=zeros(1,T-10); % initial errorc=zeros(L+1,1);
% initial conditionmu=0.001; % step sizefor i=1:T-10 e(i)=TxS(i+10+L-EqD)-c'*X(:,i+10);
% instant error c=c+mu*conj(e(i))*X(:,i+10);
% update filter or equalizer coefficientendsb=c'*X;
% recieved symbol estimation%SER(decision part)sb1=sb/norm(c);
% normalize the outputsb1=sign(real(sb1))+sqrt(-1)*sign(imag(sb1));
%symbol detectionstart=7; sb2=sb1-TxS(start+1:start+length(sb1));
% error detectionSER=length(find(sb2~=0))/length(sb2);
% SER calculationdisp(SER);% plot of transmitted symbols subplot(2,2,1), plot(TxS,'*');
grid,title('Input symbols'); xlabel('real part'),ylabel('imaginary part') axis([-2 2 -2 2])
% plot of received symbols subplot(2,2,2), plot(x,'o'); grid, title('Received samples');
xlabel('real part'), ylabel('imaginary part')% plots of the equalized symbols subplot(2,2,3),
plot(sb,'o'); grid, title('Equalized symbols'), xlabel('real part'), ylabel('imaginary part')
% convergence subplot(2,2,4), plot(abs(e)); grid, title('Convergence'), xlabel('n'),
ylabel('error signal') %% %IMPLEMENTATION OF BLIND CHANNEL USING CMA OR GODARD ALGORITHM
IMPLEMENTEDclc;clear all;close all;N=3000; % number of sample datadB=25; % Signal to noise
ratio(dB)L=20; % smoothing length L+1ChL=1; % length of the channel= ChL+1EqD=round((L+ChL)/2);
% channel equalization delayi=sqrt(-1);%Ch=randn(1,ChL+1)+sqrt(-1)*randn(1,ChL+1);
% complex channel%Ch=[0.0545+j*0.05 .2832-.1197*j -.7676+.2788*j -.0641-.0576*j .0566-.2275*j .
4063-.0739*j];Ch=[0.8+i*0.1 .9-i*0.2]; %complex channel Ch=Ch/norm(Ch);% normalizeTxS=round(rand(1,N))*2-1;
% QPSK symbols are transmitted symbolsTxS=TxS+sqrt(-1)*(round(rand(1,N))*2-1);x=filter(Ch,1,TxS);
%channel distortionn=randn(1,N)+sqrt(-1)*randn(1,N);
% additive white gaussian noise (complex) n=n/norm(n)*10^(-dB/20)*norm(x);
% scale noise powerx1=x+n; % received noisy signal...................1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.
13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.
46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.
79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.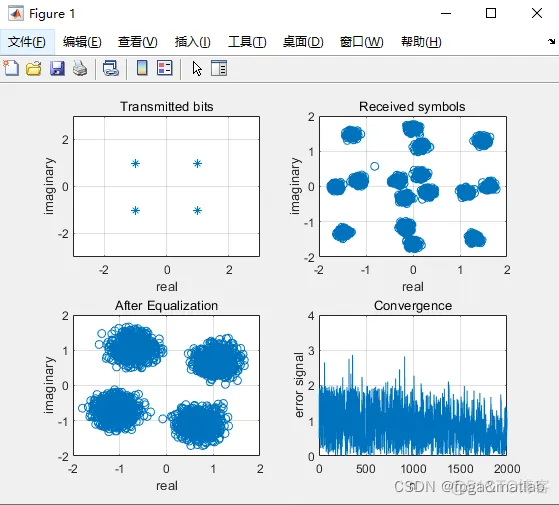
免责声明:本文系网络转载或改编,未找到原创作者,版权归原作者所有。如涉及版权,请联系删